por April Papps hace 5 años
221
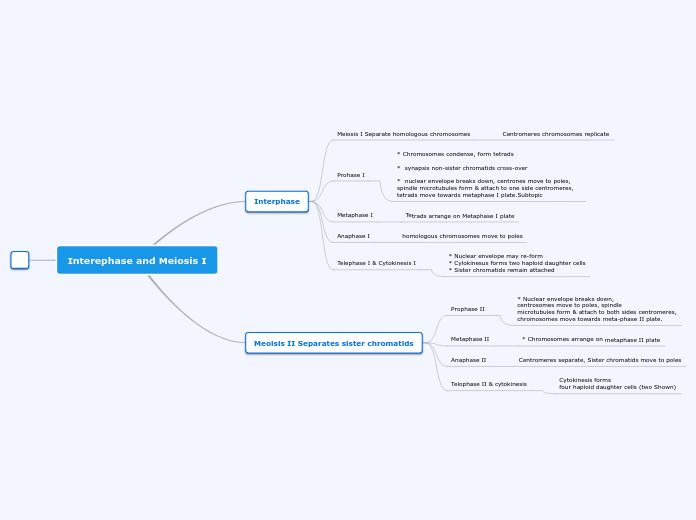
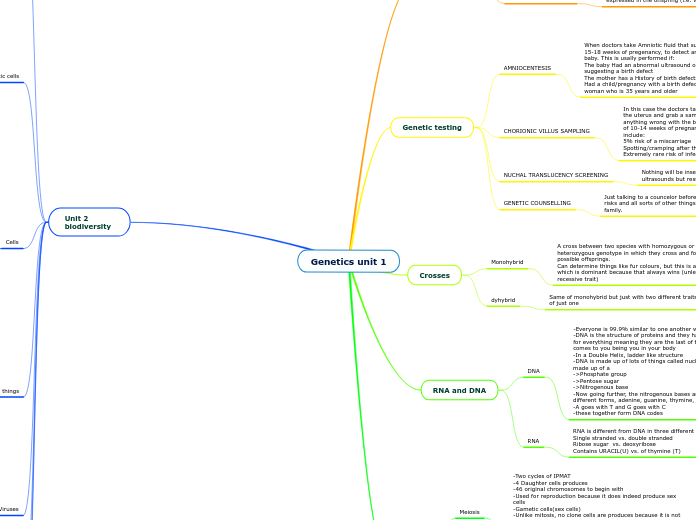
Interephase and Meiosis I
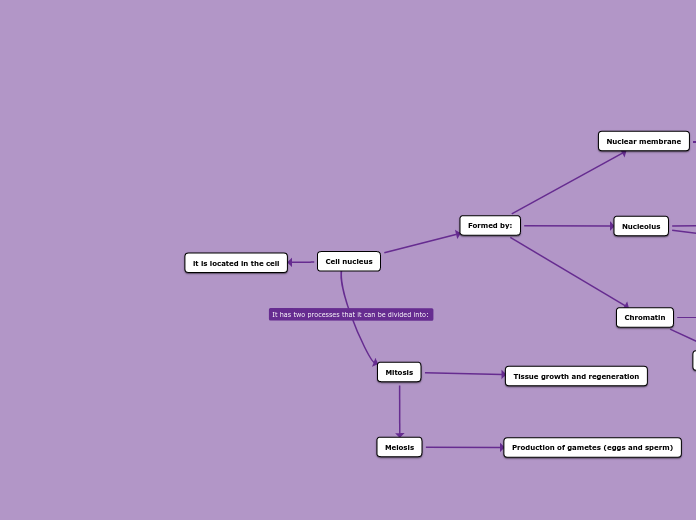
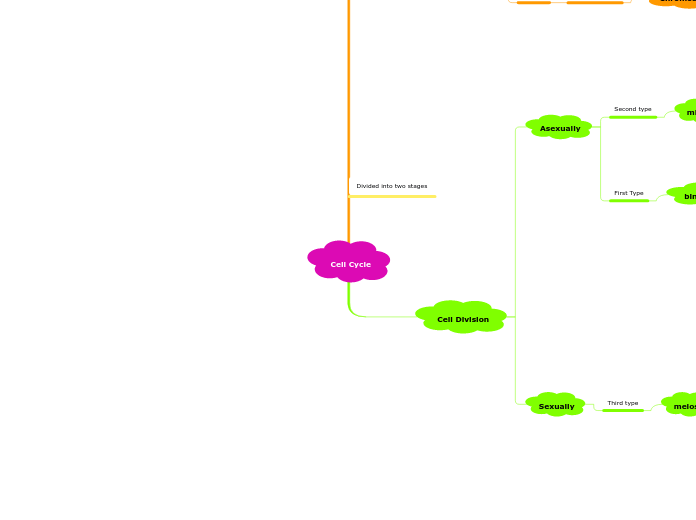
The process of meiosis is crucial for sexual reproduction and involves two distinct stages: Meiosis I and Meiosis II. During Meiosis I, homologous chromosomes are separated after undergoing processes like synapsis and crossover.