Measurement Unit
Who did what
Emma
Jessica
Alexandria
Volume
Surface Area
Area
Circle: Pi x r ^2, where r is the radius.
Trapezoid: 1/2(base a + base b), (A=1/2(a+b)x h, where h is the altitude.
Triangle: 1/2( base x height) (A=1/2xbxh, where h is the altitude)
Parallelogram: base x height (A= b x h, where h is the height)
Rectangle: Length x width (A= l x w)
Perimeter
Circle: (circumference)- 2 x Pi x r, where r is the radius (C= 2Pi(r))
The measures of each side of a shape added together.
Geometric Figures
Prisms
Prisms: Is a polyhedron in which two faces are parallel and congruent polygons, called its bases and whose other faces are parallelograms, called its lateral faces. The edges of the lateral faces are called lateral edges.
Right Prisms: Prism in which its lateral edges are perpendicular to its bases.
Pyramids: polyhedron for which one face, the base, is a polygon and all other faces are lateral faces are triangles. The apex is the top point of the pyramid.
Cylinders: It is a prism except that its bases are circles instead of polygons. A right cylinder in when the segment joining the centers of the circular bases is perpendicular to the bases.
Cones: Is a pyramid except that its base is a circle instead of a polygon.
Surface Area of Prisms is the sum of all the areas of the shapes that cover the surface of an object. Volume measures the amount of space enclosed within the boundary. B is the area of the bases, h is the height, p is the perimeter of each base, s is the slant height.
Sphere
V=4/3pir^3
SA=4pir^2
Right Circular Cones
V=1/3Bh; B is the same as pir^2
SA=pir^2+pirs
Right Regular Pyramid
V=1/3Bh
SA=B+1/2ps Slant height can be calculated with Pythagorean Theorem if it is not known
Right Cylinder
Right Prism
V=Bh
SA=2B+ph
Polygons
Circle: shape where all measurements from the center are equal.
Regular Polygons:
Quadrilaterals
Rectangles: A four sided shape where every angle is a right angle. The opposite sides are parallel and equal of length.
Rhombus: Four sided shape where all of the sides are equal in length. Opposite sides are parallel and opposite angles are equal.
Square: Has equal sides and every angle is a right angle. Opposite sides are parallel.
Parallelogram: Has opposite sides parallel and equal in length. Also opposite angles are equal.
Trapezoid: Has a pair of opposite sides parallel.
Kite: Has two pairs of sides. Each pair is made up of adjacent sides that are equal in length. The angles are equal where the pairs meet.
Triangles
Scalene:No equal sides and no equal angles.
Equilateral:Three equal angles and three equal sides. The angles will always all be 60 degrees.
Isosceles: Two equal sides and two equal angles.
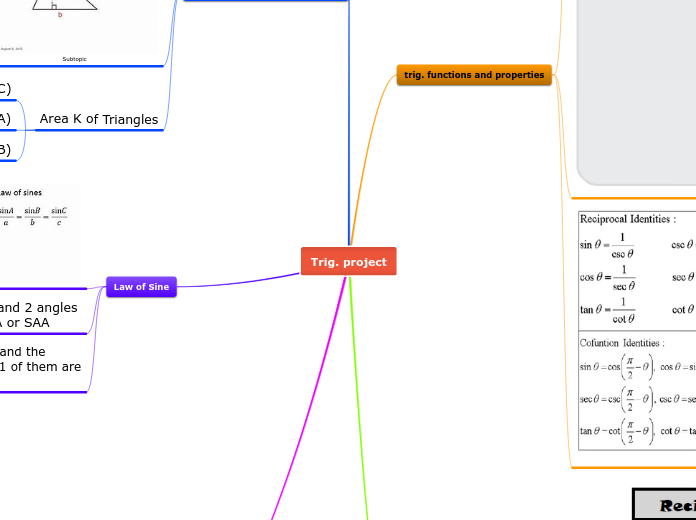
Pythagorean Theorem
If a right triangle has legs of length a and b and its hypotenuse has length c, then a²+b²=c²
C is always the longest leg
With Pythagorean Theorem you can find out the length of any side of a right triangle as long as you know the other two sides.
Angles
Angle: Is the figure formed by two rays, called the sides of the angle, sharing a common endpoint, called the vertex of the angle. Angle Measure: The given measurement of an angle which is typically in degrees. This can be found by the use of a protractor. Supplementary Angles: pairs of angles that add up to 180 degrees. Complementory Angles: Pairs of angles when added together sum to 90 degrees. Congruent Angles: When all angles are the same measurement. Verticle Angles: Angles that are equal and supplementary. Corresponding Angles: When two lines are crossed by another line, the angles are in matching corners. Angles in a triangle: All three angles must add up to 180 degrees every time.
Acute Angle: Is less than 90 degrees.
Obtuse Angle: Is greater than 90 degrees.
Right angle: Exactly 90 degrees.
Straight Angle: Will always be 180 degrees.
Interior Angle: The angle inside of a shape.
Exterior Angle: The angle outside of a shape.