por Hend Montaseb hace 5 años
150
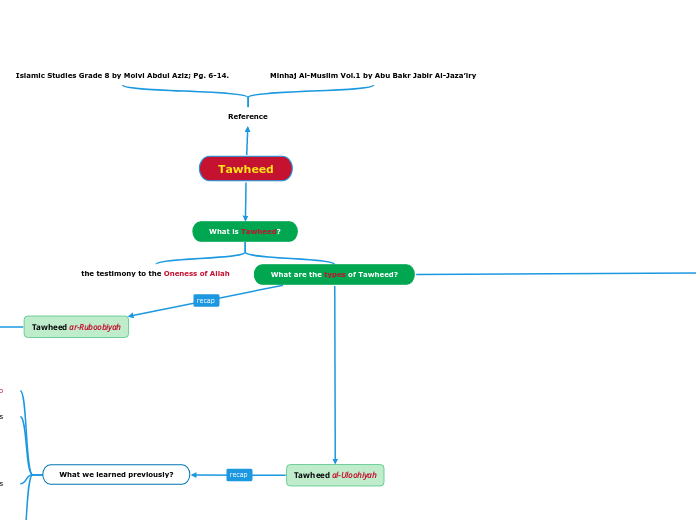
Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
The text delves into the various mechanisms through which pathogens cause damage to their host cells and how they navigate through a host's defenses. It explains the roles of exotoxins and endotoxins, detailing the specific ways these toxins disrupt host cell function.