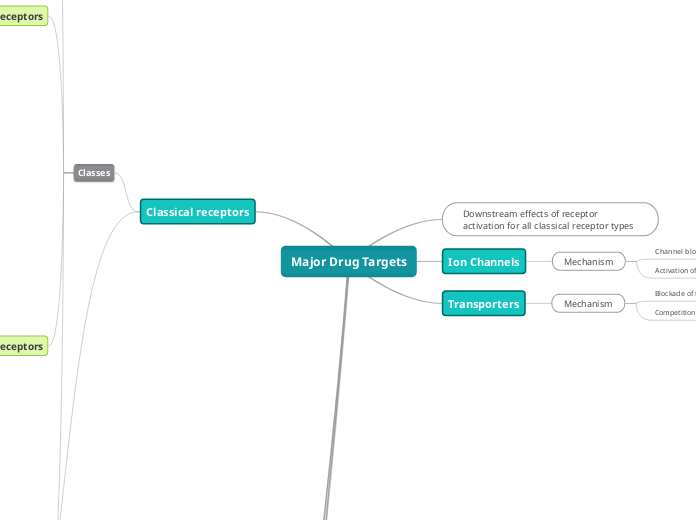
Major Drug Targets
Nucleic acids
Drugs targeting DNA and RNA metabolism
- Inhibitors of DNA/RNA regulatory proteins
- Direct interaction with nucleic acids
- Intercalating agents
- Alkylating agents
- Strand breaking agents
Enzymes
Drug activation by catalysis
Competition for catalytic site
Blockade of catalytic site
Classical receptors
General Mechanisms
Include targets for majority of prescription drugs
Encompass some groups of ion channels and enzymes
Drug shares endogenous ligand binding site
Classes
Type 4 Nuclear receptors
Subfamilies:
Hybrid
- class 2 receptors that form obligate heterodimers with RXR
- includes: thyroid hormone receptor, vitamin D receptor
Class 2
- in nucleus (induces heterodimerization with retinoid x receptors, which causes co-repressor to dissociate, and co-activator protein to bind
- include: fatty acid/cholesterol receptors, xenobiotic receptors (induces drug metabolizing enzymes-P3A)
Class 1
- in cytoplasm associated with heat shock proteins (allows class 1 receptors to dissociate from heat shock proteins and homodimerize)
- receptors for steroid hormones: glucocorticoids, mineralcorticoids, oestrogen, progesterone, androgen
Characteristics:
- Ligands include: hormones, vitamins, "orphan receptors"
- responds in hours-days
Structure:
- no transmembrane domain (2 terminal domains bound above core structure: N-terminus and C-terminus)
-found in cytoplasm or nucleus of cell
Type 3 Kinase-linked receptors
Types:
- Kinase-linked receptors
- Receptor tyrosine kinase: Growth factor receptors (epidermal and nerve) and Toll-like receptors (bacterial infection)
- Serine/Threonine Kinase: transforming growth factor receptor
- signaling cascade
- Kinase-associated receptor
- no integral kinase
- associate with cytosolic tyrosine kinase
- Jak-stat signaling pathway
Characteristics:
- Ligands include: growth factors, cytokines, insulin, bacterial LPS
- Responds in minutes-hours
Structure:
- 1 transmembrane domain: connects EC and cytoplasmic domains
- form dimer pairs when activated
- *have an additional integral enzymatic capacity in phospho-kinase domains
Type 2 G-Protein coupled receptors
Mechanism of Activation:
- ligand binds receptor to induce a conformational change
- high affinity binding sites for G protein trimer are exposed
- GDP bound to alpha subunit is converted to GTP when G protein complex binds GPCR
- GDP -> GTP releases activated alpha subunit from beta/gamma subunit complex and receptor
Subfamilies:
- Rhodopsin family
- Secretin/glucagon family
- Metabotropic glutamate receptor/ Ca sensor
Metabotropic glutamate
- small group
- GABAb receptors
Secretin/Glucagon
- receptors for peptide hormones (calcitonin, oxytocin, renin)
- intermediate EC tail with ligand binding domain
Rhodopsin
- Largest group
- mainly amine neurotransmitters, neuropeptides, purines, protanoids, cannabinoids
- short extracellular tail (N-terminal)
- ligands bind to helices or extracellular hoops
Characteristics:
- Ligands: ACh, 5HT, dopamine, opioids, etc.
- GPC receptor agonists are similar to ligand gated: RAPID effects (seconds) , but not as fast as ligand gated
- receptor desensitization
- associate with ligand-bound receptors: anchored to cytoplasmic surface of cell membranes
Structure:
- 7 transmembrane domains (alpha helices)
- extracellular and cytoplasmic domain
- trimeric: alpha subunit (G alpha s, G alpha i, G alpha q, G alpha 12), beta subunit, gamma subunit
Type I Ligand-Gated ion channels
Characteristics:
- respond extremely rapidly (millisec) to activate and recover
- controls synaptic events
- no difference to speed of transfer whether drug or biological ligand binds
- length of time pore remains open depends on ligand
Structure:
- 4 transmembrane domains of alpha helices
- Pentameric complex of subunits
- Ligands: Ach, GABA, Glutamate, 5-HT3
- Selective: central aqueous pore with high concentration of negatively or positively charged amino acids to make the pore either cation-selective (nicotinic Ach) or anion-selective, respectively.
- anion selective: GABAa receptor, 5-HT3
Transporters
Competition for transport site
Blockade of transport site
Ion Channels
Mechanism
Activation of channel
Channel blockade
Downstream effects of receptor activation for all classical receptor types