VALLEJOS TORRES,MARYLIN
ROJAS GUTIERREZ, KELLY
CASTRO ROJAS LEISLY CECILIA
BACILIO ROJAS, JANE
VIGO SALDAÑA, ANGIE
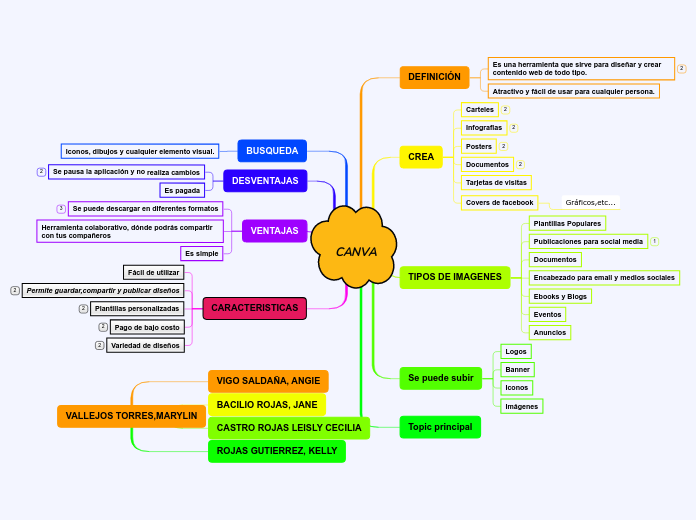
CANVA
The part of speech is a category to which a word is assigned according to its syntactic functions. In English the main parts of speech are noun, pronoun, adjective, determiner, verb, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection.
CARACTERISTICAS
A pronoun is a word that can be used in place of a noun, typically after the noun itself has already been stated.
Variedad de diseños
Relative pronouns are used to add more information to a sentence. Which, that, who (including whom and whose), and where are all relative pronouns.
Which, Where
Pago de bajo costo
Interrogative pronouns are used in questions. Although they are classified as pronouns, it is not easy to see how they replace nouns. Who, which, what, where, and how are all interrogative pronouns.
Which, Who
Plantillas personalizadas
Demonstrative pronouns are used to demonstrate (or indicate). This, that, these, and those are all demonstrative pronouns.
This, These
Permite guardar,compartir y publicar diseños
Possessive pronouns are used to show possession. The possessive pronouns are mine, yours, his, hers, ours, and theirs.
His, Your
Fácil de utilizar
The personal pronouns are I, you, he, she, it, we, they. More often than not (but certainly not always), they replace nouns representing people.
VENTAJAS
An article is a word used to modify a noun, which is a person, place, object, or idea. Technically, an article is an adjective, which is any word that modifies a noun.
Es simple
Herramienta colaborativo, dónde podrás compartir con tus compañeros
Se puede descargar en diferentes formatos
It refers directly to a specific noun or groups of nouns.
JPG
PNG
PDF
DESVENTAJAS
A conjunction is a word like 'if' 'but' or 'and' which is used to connect sentences or clauses together.
Es pagada
Se pausa la aplicación y no realiza cambios
Subordinating conjunctions are conjunctions that are used at the beginning of subordinate clauses. Some examples of these conjunctions are: although, after, before, because, how, if, once, since, so that, until, unless, when etc.
Although it was raining, I went out.
BUSQUEDA
Iconos, dibujos y cualquier elemento visual.
Topic principal
Se puede subir
Indefinite articles are the words 'a' and 'an.' Each of these articles is used to refer to a noun, but the noun being referred to is not a specific person, place, object, or idea. It can be any noun from a group of nouns.
Imágenes
Iconos
Banner
Logos
TIPOS DE IMAGENES
An adjective is a word that's used to describe a specific noun and to provide more detail to the listener.
Anuncios
Eventos
Ebooks y Blogs
Encabezado para email y medios sociales
Publicaciones para social media
Superlative adjectives demonstrate a higher level of comparison between entities.
Plantillas Populares
Expresses a comparison between two entities or groups of entities in quality or degree.
CREA
A noun is defined as a person, place, thing or idea. Proper nouns always begin with a capital letter. Common nouns, which are general words, such as 'cars,' are not capitalized.
Covers de facebook
Gráficos,etc...
Tarjetas de visitas
Documentos
Compound nouns are words where two nouns have been stuck together to make a new noun. Compound nouns should be written as one word, without a hyphen.
Candlestick
Posters
A noun which refers to a group of things/people.
Family, Class
Infografias
Countable nouns are nouns that can be counted, even if the number might be extraordinarily high.
Uncountable nouns are nouns that come in a state or quantity which is impossible to count; liquids are uncountable, as are things which act
like liquids.
Cats, Rain
Carteles
Proper nouns are the names of specific people or places. They should always begin with a capital letter.
Mary, Paris
DEFINICIÓN
A verb is an action word or 'doing' word that signifies movement in some way.
Atractivo y fácil de usar para cualquier persona.
Es una herramienta que sirve para diseñar y crear contenido web de todo tipo.
A verb with its own meaning: a verb that is not an auxiliary verb.
Create sentences
They have it.