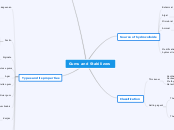
Gums and Stabilizers
Relative Ranking of Gums
Suspension Ability
Suspension Requires a Gelling Agent
Chocolate milk - carrageenan
Salad dressing - Xanthan, Pectin
Processed Fruits - Pectin
Gums with Useful Protein Reactivity
Pectin (pH< 4.6)
Carrageenan (pH> 4.6)
Natural vs Not Natural
Not Natural
MC
HPC
CMC
PGA
LMA Pectin
Natural
HMP & LMP
Carrageenan
Tragacanth, Karaya
Agar, Gelatin
Na alginate, Guar, Tara
Xanthan, Gellan
Konjac, Arabic
LBG
Gelling vs Thickening
Thickening
Guar
LBG
CMC
PGA
Arabic
Tara
Tragacanth
Karaya
Xanthan
Gelling
Pectin
Carrageenan
Gellan
Agar
Methyl Cellulose
Na alginate
Konjac
Gelatin
Hydrocolloids Solubility in Various Temp.
Special cases
Konjac
Swell below 90
Soluble at temp. 90?>
Agar
Not soluble below temp. 70 and swell at 70
Soluble at temp. 90/>
Gelatin
Soluble in temp. above 25 and swell at 25
Soluble in all temp. about range 25-90/>
Guar
Arabic
Xanthan
CMC
Pectin *85-90% soluble in temp. 25
Solution Clarity
Guar
Starch
LBG
Xanthan
Polyproplyene Alginate
Konjac
Microcystalline cellulose
Good
Pectin
Refined LBG
Cellulose
Carrageenan
Gellan
Gum Arabic
Gelatin
Agar
Acid stability (pH<4.0)
Fair
Guar
PGA
MCC
Gelatin
Alginate
Agar
Poor
Carrageenan
Cellulose derivatives
Excellent
Pectin
Xanthan
Gellan
LBG
Tragacanth
Main Classes of Hydrocolloids
Microbial Gums
Xanthan Gums - polyssaccharides from the fermentation of CHO substrate with Xanthomonas campestris
Thickening, suspending and stabilizing effects
Pseudoplastic - thin with shear and recover their initial viscosity when shearing stops - important for good flavour release, mouthfeel
~Completely soluble in cold water
~Viscosity - High viscosity at low concentration
~Stable to heat and pH - Remain unchanged across temp. range 0-100, pH 1-13
Extract from tubers
Konjac glucomannan
Extract from seaweeds
Alginate
from brown seaweed (Laminaria hyperborea), made up of blocks of D-mannuronic acid (M-block) and L-guluronic acid(G-block)
Propylene glycol alginate (esterified form of alginate)
stabilize emulsion
e.g: mayonnaise/ low-fat mayonnaise
Thickener in beverages
e.g: dry mix fruit drinks, gives fast hydration and mouthfeel
Stabilizing effect in frozen products
e.g: ice cream to avoid crystallization, gives homogenous breakdown without whey separation
Properties
*Ratio of M:G and MW of polymer determine the solution and gelling properties
Can form gel in cold water in the presence of Ca ions,
*gel are thermoreversible
High G alginate forms strong, brittle gel with good heat stability
Carrageenan - from seaweed of the rhodophyta family, composed of linear galactan polyssaccharides that have a sulfate content of 15-40%
Type of Carrageenan
Lambda, repeating of D-Galactose-2-Sulphate and D-Galactose-2,6-Disulphate with 35% of sulphate content
Kappa, repeating unit is D-Galactose-4-Sulphate linked with 3,6-anhydrous-D-Galactose with 25% of sulphate content
Iota, repeating unit is D-Galctose-4-Sulphate linked with 6-anhydrous-D-Galactose-2-Sulphate with 32% of sulphate content
Gelation of Carrageenan
Kappa and iota carrageenan has the ability to form thermoreversible gels upon cooling of hot aqueous solution containing various cation
Lambda carrageenan do not gel because it structure does not allow double helices formation
Structure of kappa & iota allow the two molecules to form double-helices-like structure, a chain molecules in 3-D network, a gel
Cations are important. Calcium ions and potassium ions form bridges between adjacent double helices through an electrostatic binding in two adjacent sulphate groups so, it stabilize and strengthening the network.
Extract from seed
Guar gums - linear chain of mannose with single galactose units attached as side chains
Very stable from pH 4-10
More highly substituted than LBG
*more soluble, hydrates fully in cold water giving high viscosity
Nongelling
*mainly used as viscosity builder, stabilizers and water binder
Locust bean gums - from the seed of carob bean, seed of the leguminose Ceratonia siliqua (indigenous to Mediterranean countries)
Canned foods, sauces, desserts, beverages, ice cream, processed meat
Primary function:
thickening,
emulsion stabilizer,
inhibit syneresis
Non-ionic, stable over pH range 3.5- 11.0
Does not form gel by itself
*combined with xanthan gums to gel
Maximum viscosity develop when heated to 95 degree Celsius, then cooled
Insoluble in cold water
*must be heated to dissolve
Galactomannan gums
*made up of mannose and galactose, in ratio of 4:1
Extract from part of plants
Cellulose Derivatives - chemically modified cellulose through alkaline treatment that converts cellulose into an ether.
E.g: carboxymethylcellulose (CMC), hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC)
Use in fried food to:
create barrier to oils absorption,
retard loss of moisture,
improve adhesion of batter
Methylcellulose (MC) and HPMC gel when heated.
It also returns to origial liquid viscosities when cooled
Very clear solution,
Stable over pH 4-10
Pectin - from peel of citrus fruits/ apple pormace
Gelation of Pectin
HMP: gels at high solids, low pH
HMP: DE increase, gelling ability increase
LMP: forms gel with calcium ions, loses ability as DE increases
Type of Pectin
Low Methoxyl Pectin (LMP)
Application
Heat reversible
*utilised in bakery jams, jellies for glazing purpose
Used in jams with soluble solids <55%
*low calories jam, jellies preserves
Formation of Gel
"egg-box" model
1. chain segment with 14/> residues having a ribbon-like symmetry forms parallel-oriented aggregates.
2. Calcium ions fit into cavities in the structure.
3. Chelate bonds with Oxygen from both galacturonan chains formed by calcium ions are formed.
Wide pH range (1-7)
*soluble solid can be up to 85%
Low solid content
Presence of Calcium ions
DE < 50%
Amidated LMP (ALMP)
*very reactive calcium ions , assist gelation in low sugar food preparation; e.g: low-sugar jams and jellies
Conventional LMP
*less reactive calcium ions than ALMP, used as thickening agent in yogurt fruit
High Methoxyl Pectin (HMP)
Structure
Excellent flavour release
Clear and transparent
Not heat reversible
Firm and short structure
Setting times from 1-3 mins to more than 1 hr
DE- 58-75%
Classified further into
slow set (DE as low as 58)
Suitable to very acid fruits
*to avoid premature gelation
ultrarapid/ rapid set (DE as high as 77)
Used in jams with whole fruits
*to ensure uniform distribution of fruits particles
Formation of gel
Effect of pH in gelation
Rapid sey pectin will set at higher pH, higher temperature than slow set pectin
High DE, less soluble solid, higher pH which gels can be formed
pH= About 2.8-3.8
Soluble solid content= About 55-85%
Derivatives from exudation/ sap/ trees
Gum Arabic/ gum acacia - sap exuded from various species of Acacia trees
Uses
Soft drink emulsion
*As emulsifier and stabilizers
Foam in beer
*promote stabilization
Encapsulation agent
*to encapsulate visible flavour compounds
Used in confectionery products
*to retard sugar crystallization, promote emulisification
Properties
Least viscous
Easily dissolve in hot/cold water
*most soluble of all hydrocolloids, 55% solid conc. can be used
Food hydrocolloids - a range of polyssaccharides and protein, known as 'water soluble gums', 'gums', 'stabilisers'
Factors affecting GUMS
Side Chain
Distribution
Number
Type
Monosaccharides composition
Molecular weight
Structure of hydrocolloid
High MW polymer, long chain sugar units with branches. Branches will determine ionic or non-ionic gums
Degree of Polymerization (DP)
Lower DP - Low viscosity, faster to hydrate
Higher DP - High viscosity, slower to hydrate
Degree of Substitution (DS)
Lower DS - Slower to hydrate
Higher DS - Faster to hydtrate
Used less than 2% in food
Functions
Secondary
Film formation
Encapsulation
Crystallization contoller
Suspension of particulates
Emulsion stabilizers
Primary
Gelling/ Texturizing agents
Thickening agents