Sociology Chapter 4 - Socialization
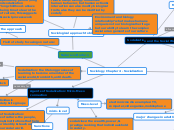
Agents of Socialization: Micro-Meso connection
Meso-level
electronic media examples: TV, computer,videogames, mobilephone
social class: the wealth, power, & prestige ranking that individuals hold in society.
micro-level
Sanctions
Positive, when children rewarded for good behavior with a smile, praise, cookies or special event. negative, when they receive a verbal reprimand or a slap on the hand, be sent to their room.
Def Agents of Socialization: transmitters of culture-the people, organizations, & institutions that help us define our identity & teach us how to thrive in our social world.
way self learns values, beliefs, and behaviors of culture
Two types of agents of socialization
1) formal agents (family, school, teachers, religious training)
2) informal agents (media, books, advertising, internet)
Development of Self: Micro-level Analysis
Resocialization is the process of shedding one or more positions & taking on others, which involves learning new norms, behaviors, & values suitable to the newly acquired status.
major changes in adult life
total institutions: a place that cuts people off from the rest of society & totally controls their lives in the process of resocialization. Ex: prison, mental hospitals, monasteries, concentration camps, boarding school, military barracks.
Lifecycle
Def rites of passage - celebrations or public recognition when individuals shift from one status to another
Different from culture to culture
Provide examples from Kazakhstani culture of significant rites of passages, when people are married, the girl life will change completely, her culture and society.
Change from one lifecycle stage to another from birth to death
Def: Self the perceptions we have of who we are
Core self - a stable inner sense of who we are regardless of the immediate setting in which we find ourselves
Mead
Significant others- parents, guardians, relatives, or siblings whose primary & sustained interactions with the child are especially influential. generalized others- this process gradually builds up a composite of societal expectations that the child learns from family, peers, & other organizations.
3 critical stages in the development of self
1) imitation stage
2) play stage
3) game stage
Parts of the self
focused on by Chicago School emphasize the role of I, focuses on individual's involvement in their own development & their agency in creating their world.
?
focused on by Iowa School, more emphasis on the Me-on the role of others & external social environment in shaping us.
Humans think in symbols
Symbols are actions or objects that represent something else & therefore have meaning beyond their own existence.
Examples of symbols: language & gestures
Role-taking: individuals take others into account by imagining themselves in the position of that other
Cooley and the looking-glass self
3 main elements (hint: Fig 4.1)
1)we imagine how we want to appear to others
2) others make judgments & respond
3) we experience feelings & react based on our interpretations
Def: Looking-glass self is a reflective process that develops the self-based on our interpretations & on our internalization of the reactions of others.
Hereditary blueprint interacts with family and culture
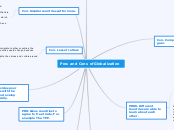
Socialization and the Social World
Macrolevel
Ex: National television ads or government bureaucracy are part of socialization (lifelong process) experience that teaches us how to function in our society.
Conflict Perspective, the linkages between various parts of the social world are based on competition with or even direct opposition to another part.
Structural-Functional Perspectives of socialization tend to see organizations at different levels supporting each other
Mesolevel
educational systems teach the knowledge & skills necessary for functioning in society
religious denominations & political groups teach their versions on the truth
Microlevel
Peer Groups: who are roughly equal in age or accupation within the society
Parents teach children proper behaviors to be succesful in live
Nature vs Nurture
Sociological approach to biology
gestation/dependency period (long childhood) and socialization relationship? long childhood-allows each human being time to learn the complexities of culture, this suggests that biology & social process work together.
Problems of inadequate care? deprivation & isolation on normal socialization.
Environment and biology relationship? what makes humans unique is not our biological heritage but our ability to learn the complex social arrangements of our culture
Biology and human behavior relationship? biology influences human behavior, but human action & interaction can also modify biological traits, also they can be modified by society
Field of study focusing on nature:
Limitations of the approach
Socialization: the lifelong process of learning to become a member of the social world, from birth, until death.
1) survival of individuals
2) survival of society & its groups
Interaction is basic building block
3 main elements
human biological potential
culture
individual experience