por Diego Ariza hace 5 años
358
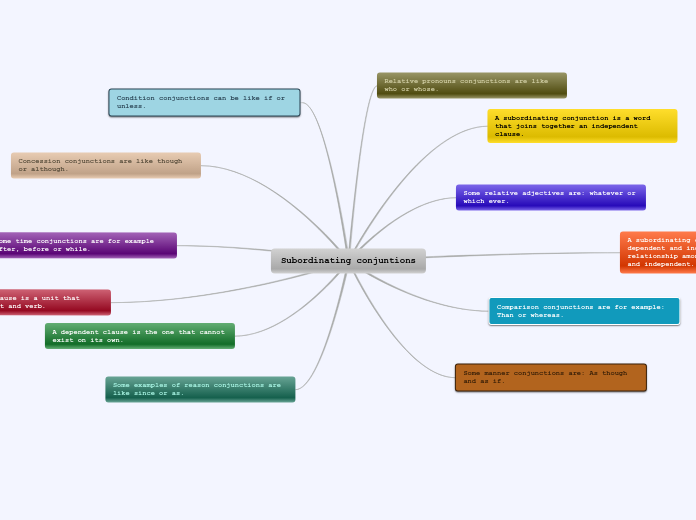
Special Project: Grammar
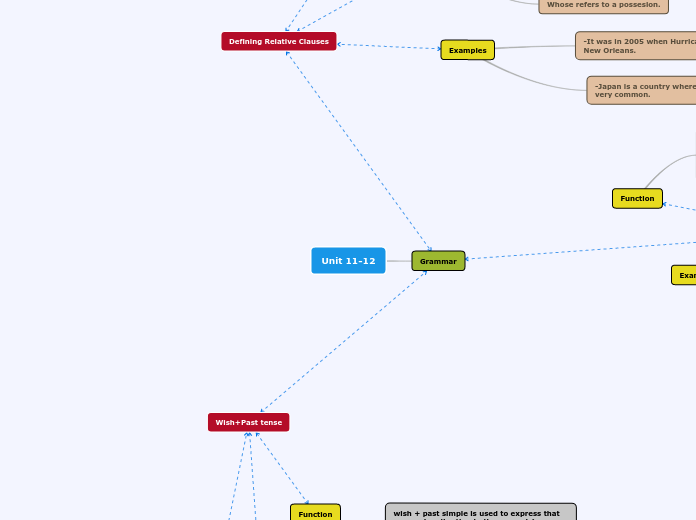
The content discusses the use of relative clauses and conditional sentences in English grammar. Relative clauses, which start with relative pronouns like who, that, which, whose, where, and when, are used to define or identify the noun that comes before them.