The Skeletal System
Diseases + Disorders
Arthritis
cartilage covering the ends of bones wear out, results in increased friction b/w bones
inflammation of joints
Bursitis + Tendinitis
do not heal quickly due to low blood supply
caused by injuries, blows to the joints or bacterial infections
inflammation
response to injury characterized by redness, warmth, swelling + pain
Sprains
take long time to heal because the ligaments have few cells + poor blood supply
accompanies by internal bleeding, bruising, swelling + pain
damage to ligaments
Osteoporosis
decline in estrogen after menopause can cause it
slight imbalance b/w rates of osteoclasts (breaking down bone) + osteoblasts (making new bone)
caused by excessive bone loss
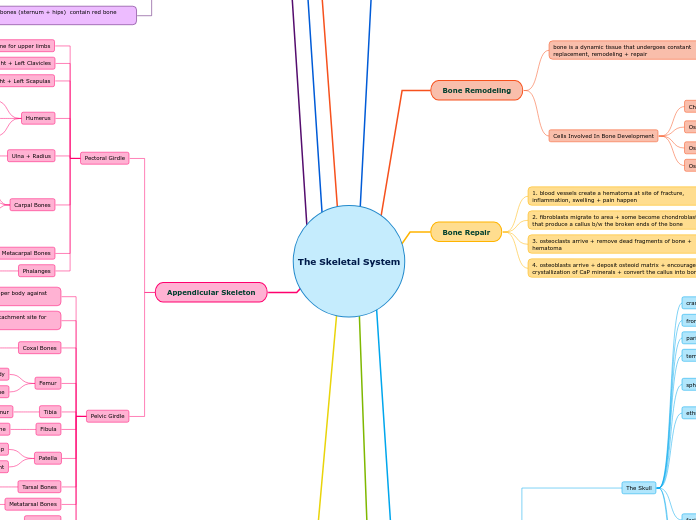
Appendicular Skeleton
Pelvic Girdle
broader in women
14 bones that form the toes
Metatarsal Bones
5 long bones that form the foot
Tarsal Bones
7 ankle + heel bones
Patella
triangular bone that protects + stabilizes knee joint
kneecap
Fibula
smaller lower bone
Tibia
larger lower bone that is in contact w/ femur
Femur
rounded upper end of each fits into socket in coxal bone
longest + strongest bone in body
Coxal Bones
attach to sacral region of vertebral column + then curve forward to meet in front at the pubic symphysis where they are joined by cartilage
protects organs inside pelvic cavity + is attachment site for legs
primary function is to support weight of upper body against force of gravity
Pectoral Girdle
Phalanges
14 bones that form the fingers + thumb
Metacarpal Bones
5 bones that form the palm of the hand
Carpal Bones
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
often due to repetitive typing on a computer keyboard
repetitive stress syndrome
held together by sheath of connective tissue
8 small bones that make up the wrist
Ulna + Radius
forearm bones
Humerus
long bone
upper arm
fits into a socket in the scapula
Right + Left Scapulas
triangular bones in upper back
Right + Left Clavicles
extend across top of our chest
supportive frame for upper limbs
The Human Skeleton
flat + irregular bones (sternum + hips) contain red bone marrow
irregular bones
don't fit into the other categories
coxal bones + vertebrae
flat bones
thin, flattened bones with small amount of spongy bone b/w compact bone
cranial bones + sternum
short bones
wrist bones
wide as they are long
long bones
bones of limbs + fingers
Functions of the Skeleton
permits flexible movement of most parts of the body
protects certain organs from physical injury
serves as structural framework for support of soft organs
Bone Cell Regulation
when Ca levels RISE
calcitonin stimulates osteoblast activity which causes Ca + P to be removed from blood + deposited into bone
when Ca levels FALL
PTH stimulates osteoclasts to secrete bone-dissolving enzymes to release Ca + P into bloodstream
regulated by hormones
Joints
Synovial Joints
held tightly together by ligaments + stabilized by tendons
can withstand tremendous use
Ball + Socket Joint
wide range of movement
Hinge Joint
allows movement in one plane
knee + elbow
knee also includes 13 bursae sacs
to reduce friction, there are small disks on either side of knee joint called menisci
two bones are fastened together + stabilized by ligaments
bones are separated by thin fluid filled cavity
synovial membrane + surrounding hyaline cartilage create a joint capsule
articulating surfaces of two bones covered with tough smooth layer of hyaline cartilage
interior is lined with synovial membrane secretes synovial fluid to lubricate + cushion joint
Cartilaginous Joints
vertebrae + ribs
slightly moveable + allow some flexibility
bones are connected to hyaline cartilage
Fibrous Joints
fontanels
soft spots on baby's heads that change shape
immovable
Axial Skeleton
The Ribs + Sternum
shields heart, lungs + other thoracic region organs
helps us breathe by expanding + contracting
have 12 ribs
11-12 are floating ribs
have no attachment
8-10 are false ribs
attach via cartilage
1-7 are true ribs
attach directly to sternum
The Vertebral Column
Intervertebral Disks
strong impacts can cause herniated disks
permit limited degree of movement
shock absorbers
composed of fibrocartilage
separate vertebrae
contains 33 vertebrae
4 fused coccygeal
vestigial structure
5 fused sacral
5 lumbar
12 thoracic
7 cervical
supports head, protects spinal cord + serves as site of attachment for limbs + muscles
main axis of body
The Hyoid Bone
serves as point of attachment for muscles of tongue, larynx + pharynx
attached to temporal bone by ligaments
does not make direct contact with other bones
The Skull
foramen magnum
where vertebral column connects to the skull + spinal cord enters skull to communicate w/ brain
large opening at base of skull
occipital bone
back + base of skull
facial bones
mandible
attached to the temporal bone only
lower jaw + teeth
lacrimal bones
tiny opening where the tear ducts drain tears from the eye sockets into the nasal cavity
nasal bones
upper bridge of nose
zygomatic bones
cheekbones + outer portion of eye sockets
vomer bone
divides nose into left + right
part of the nasal septum
palatine bones
roof of the mouth
also formed by maxilla bones
maxilla
part of the eye sockets + anchor upper teeth
front of the skull
ethmoid bone
eye sockets + supports the nose
sphenoid bones
forms back of both eye sockets
b/w frontal + temporal bones
temporal bones
lower left + right sides of the skull
parietal bones
upper left + right sides of the skull
frontal bone
forehead + upper eye sockets
cranial bones
flat bones that enclose + protect the brain
Bone Repair
4. osteoblasts arrive + deposit osteoid matrix + encourage crystallization of CaP minerals + convert the callus into bone
3. osteoclasts arrive + remove dead fragments of bone + hematoma
2. fibroblasts migrate to area + some become chondroblasts that produce a callus b/w the broken ends of the bone
1. blood vessels create a hematoma at site of fracture, inflammation, swelling + pain happen
Bone Remodeling
Cells Involved In Bone Development
Osteoclasts
bone dissolving cells
Osteocytes
mature bone cells that maintain the structure of a bone
Osteoblasts
young bone forming cells that cause hard extracellular matrix of bone to develop
Chondroblasts
cartilage-forming cells that build a model of future bone
bone is a dynamic tissue that undergoes constant replacement, remodeling + repair
homeostasis of bone structure depends on the balance of osteoclast + osteoblast activity
OSTEOPOROSIS
condition in which bones lose great deal of mass because of an imbalance over many years in the rates of osteoclasts + osteoblasts
weight bearing exercise increases overall bone mass + strength
compression stress on a bone causes electrical currents within the bone that stimulate the bone forming activity of osteoblasts
consists of bones, ligaments + cartilage
CARTILAGE
ELASTIC CARTILAGE
lends structure to outer ear + epiglottis
highly flexible
mostly elastin
HYALINE CARTILAGE
covers ends of mature bones in joints creating smooth low friction surface
forms embryonic structures that then become bone
controlled by hormones (growth hormone)
4. growth plates in long bones move farther apart + the bone lengthens + widens
3. osteoblasts secrete osteoid + enzymes, facilitating the deposition of hydroxyapatite crystals
conversion of cartilage to bone is concentrated INSIDE growth plate
2. cartilage starts to dissolve + periosteum begins to develop, new blood vessels transport osteoblasts into area to form periosteum
1. chondroblasts form hyaline cartilage, creating a rudimentary model of future bone
chondroblast activity is concentrated OUTSIDE growth plate
smooth glossy cartilage of thin collagen
FIBROCARTILAGE
intervertebral disks + menisci
withstands pressure + tension
collagen arranged in thick bundles
found where support under pressure is needed + movement is necessary
smoother + more flexible than bone
specialized connective tissue made of collagen + elastin in a ground substance + reduces friction in joints
LIGAMENTS
confer strength to certain joints while still permitting movement in relation to each other
attach bone to bone
consist of dense fibrous connective tissue + bind bones to each other
BONES
outer surface is called the periosteum
tough layer of connective tissue that contains specialized bone forming cells
long bones like the arms and legs contain red bone marrow
stem cells in red bone marrow produce red + white blood cells + platelets
central cavity in diaphysis is filled with yellow bone marrow
primarily fat that can be used for energy
less dense spongy bone fills inner region of epiphysis
osteocytes do not need to rely on central canals for nutrients + waste removal
slender trabecular structure of spongy bone gives each osteocyte access to nearby blood vessels in red bone marrow
as hard as compact bone, but is less dense + allows for bone to be light + strong
latticework of hard + strong trabeculae
dense compact bone forms the shaft + covers each end
made up of extracellular deposits of calcium phosphate surrounding + enclosing cells called osteocytes
as bone develops + becomes hard, osteocytes become trapped in lacunae
waste products are exchanged in in opposite direction + removed by blood vessels
remain in contact with each other via canaliculi
within it are extensions of the cell cytoplasm in adjacent osteocytes joined together by gap junctions
by exchanging nutrients across gap junctions, osteocytes can be supplied with nutrients even though most osteocytes are not located near a blood vessel
channels that permit movement of ions, water + other molecules b/w adjacent cells
ones near the center of an osteon receive nutrients by diffusion from blood vessels that pass through a central canal
arranged in rings in osteons
also called Haversian Systems
nearly a solid structure w/ central canals containing nerves + blood vessels
Contains 5 Functions
Mineral storage
Blood cell formation
Movement
Protection
Support
actually a living tissue containing several cells, nerves + blood vessels
consist of nonliving extracellular calcium minerals
gives bones hard + rigid appearance
hard elements of the skeleton