por Milena Tesfay hace 2 años
211
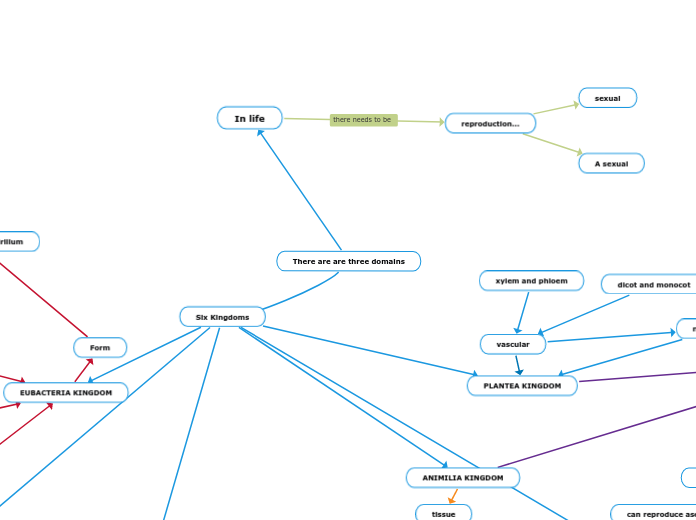
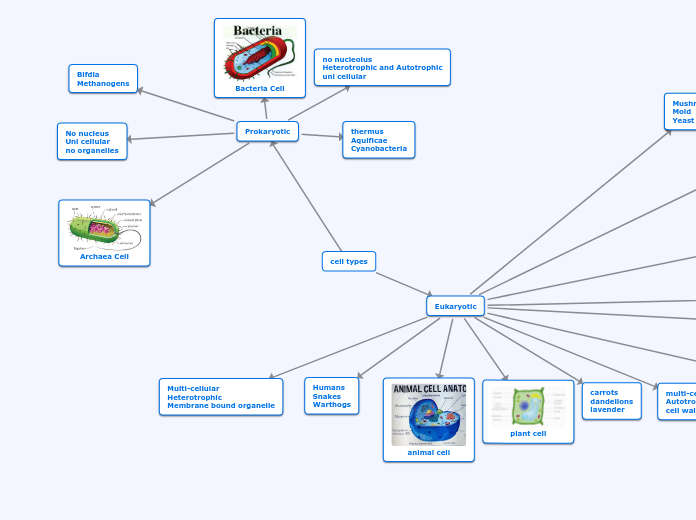
There are are three domains
Living organisms exhibit a variety of characteristics and reproductive strategies. They can be obligate anaerobes, facultative aerobes, or obligate aerobes, depending on their respiration requirements.