por Sarah Chapman hace 5 años
735
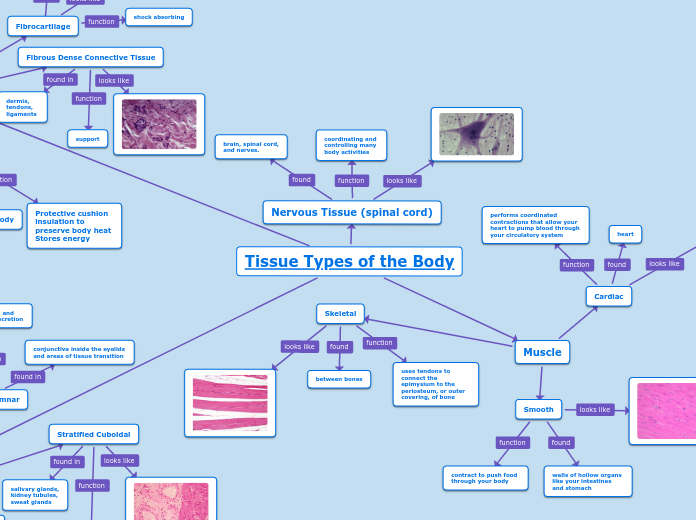
Tissue Types of the Body
The human body comprises various tissue types, each with specific roles essential for maintaining body functions. Connective tissues, including areolar, hyaline cartilage, bone, elastic cartilage, blood, and adipose tissues, provide structural support, protection, and storage functions.