por Darian Wilson hace 5 años
212
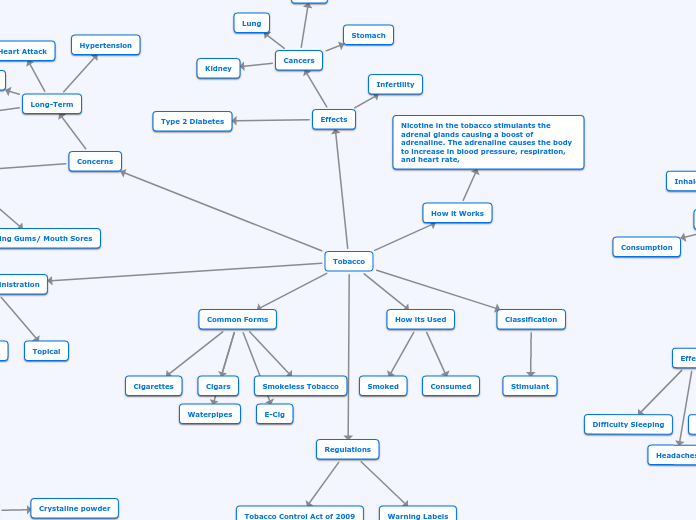
Tobacco
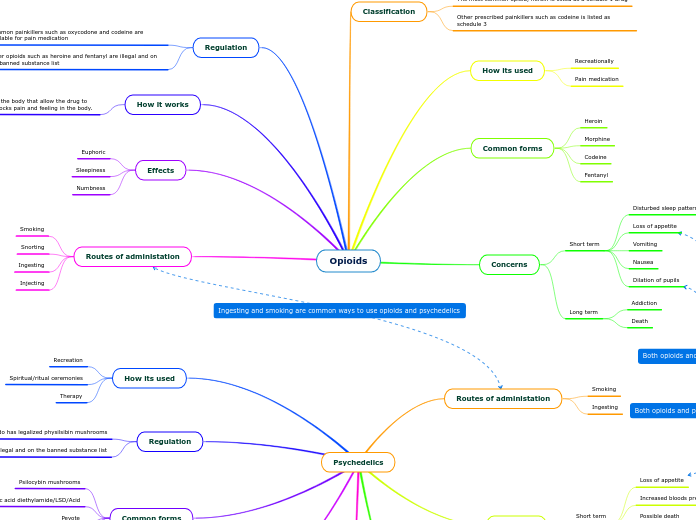
Psychedelics and benzodiazepines like Valium have diverse effects and uses. Psychedelics, classified as hallucinogens, can be consumed in various forms including blotting paper, powder, and tablets, and administered through methods such as sublingual, injection, and oral.