Unidad 3: Esfuerzos en ejes y vigas
Type in the name of the book you have read.
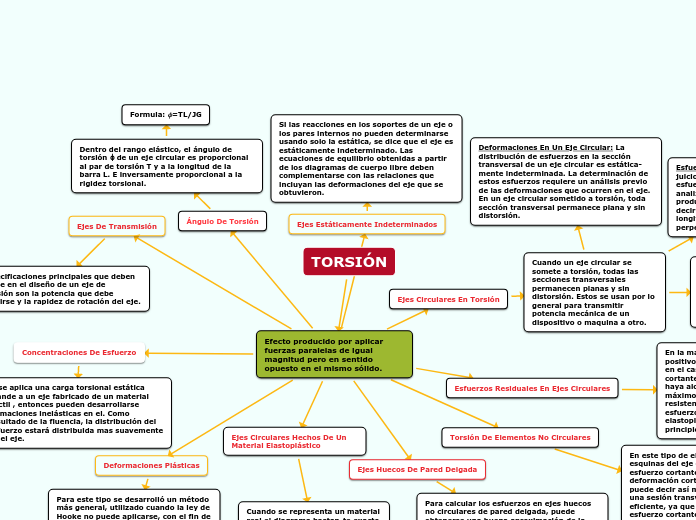
EJES ESTÁTICAMENTE INDETERMINADOS
Debido a que la estática no es suficiente para determinar los pares internos y externos.
Las ecuaciones de equilibrio deben complementarse con relaciones que involucren las deformaciones del eje y que se obtengan considerando la geometría del problema.
Take notes while you read the book. Write here your favorite quotes from the book.
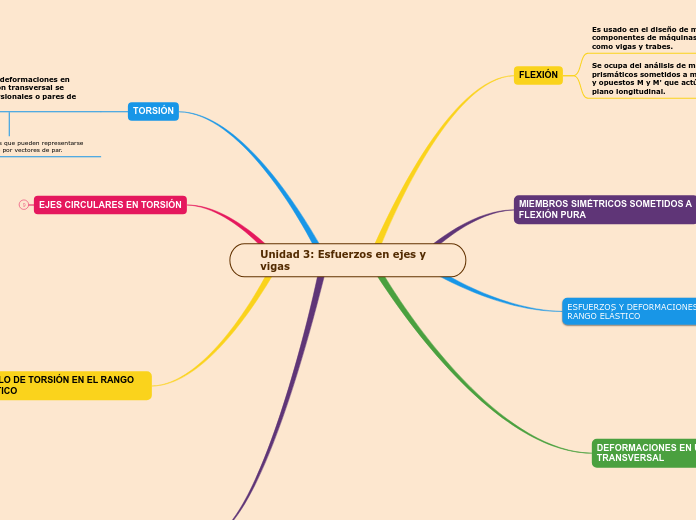
ANGULO DE TORSIÓN EN EL RANGO ELÁSTICO
Take notes while you read the book. Type here the resources, books, or websites that the author mentioned and you want to check out later.
La ecuación proporciona un método conveniente para determinar el módulo de rigidez.
Es la relación entre el ángulo de torsión ϕ de un eje circular y el par de torsión T ejercido sobre el eje.
EJES CIRCULARES EN TORSIÓN
Type the main events of the book, classifying them in: events from the beginning, events from the middle, and events from the end of the book.
Describe the story visually. Add a representative picture for each of them.
ESFUERZO EN EL RANGO ELASTICO
Los esfuerzos en el eje permanecerán por debajo del límite de proporcionalidad y también por debajo del límite elástico.
Cuando el par de torsión T es tal que todos los esfuerzos cortantes en el eje se encuentran por debajo de la resistencia a la cedencia τY.
Type the main events from the end.
Add a representative picture for each of them.
DEFORMACIONES EN UN EJE PARTICULAR
Cuando su apariencia es la misma cuando se ve desde una posición fija y se gira alrededor de su eje por un angulo arbitrario.
Un eje circular es simétrico
Si un eje circular se somete a torsión, toda sección transversal permanece plana y sin distorsión.
Type the main events from the middle.
Add a representative picture for each of them.
ESFUERZO DE UN EJE
Las condiciones de equilibrio requieren que el sistema de estas fuerzas sea equivalente a un par de torsión interno T, igual y opuesto a T'
Type the main events from the beginning.
Add a representative picture for each of them.
TORSIÓN
In contrast to the main idea, the theme is the message, lesson or moral of the book.
Some tips to find out the theme of the book easier:
- Try to find it while you are reading. It may be stated or implied.
- Think about how the characters reacted to obstacles.
- Think about the important decisions that the characters made.
- Think about the characters growing or changing throughout the book.
Son los esfuerzos y deformaciones en elementos de sección transversal se someten a pares torsionales o pares de torsión.
Son cantidades vectoriales que pueden representarse mediante flechas curvas o por vectores de par.
DEFORMACIONES EN UNA SECCIÓN TRANSVERSAL
Who is the author of the book? Type in his/her name.
En un miembro de sección transversal rectangular, la expansión y contracción de los diversos elementos en la dirección vertical se compensarán y no se observará ningún cambio en la dimensión vertical de la sección transversal.
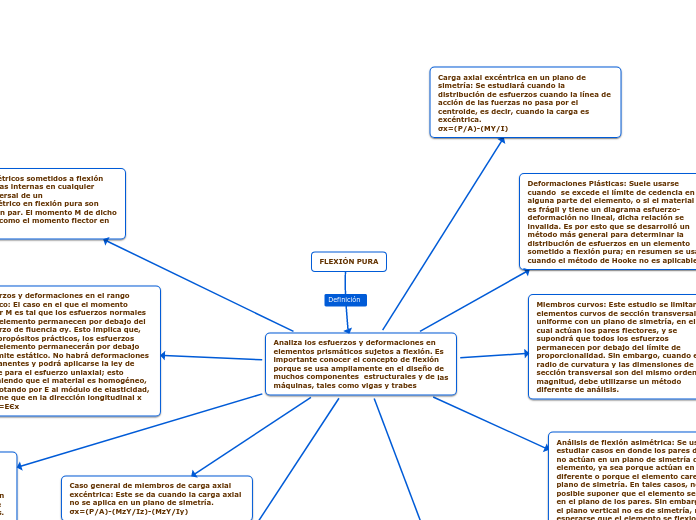
ESFUERZOS Y DEFORMACIONES EN EL RANGO ELÁSTICO
El momento flector M es tal que los esfuerzos normales en el miembro permanecen por debajo de la resistencia a la cedencia σY.
MIEMBROS SIMÉTRICOS SOMETIDOS A FLEXIÓN PURA
DEFORMACIONES
El miembro se flexionará por la acción de los momentos, pero permanecerá simétrico con respecto a dicho plano.
Sus extremos se someten a momentos iguales y opuestos M y M' que actúan en el plano de simetría.
MOMENTO INTERNO Y RELACIONES DE ESFUERZO
The main idea is what the book is mostly about.
Some tips to find out the main idea of a book easier:
- Read the title.
- Look for the text features.
- Figure out if you are reading a fiction or a non fiction book.
- Think about some examples that support this idea.
FLEXIÓN
Type the names of the book characters. Start with the main character.
Draw arrows to represent the relationship between them and if it is possible write on them what they represent for each other (if they are relatives, friends, lovers, enemies etc.)
Se ocupa del análisis de miembros prismáticos sometidos a momentos iguales y opuestos M y M' que actúan en el mismo plano longitudinal.
Es usado en el diseño de muchas componentes de máquinas y estructurales, como vigas y trabes.