por JP Tenser Jessy hace 1 año
128
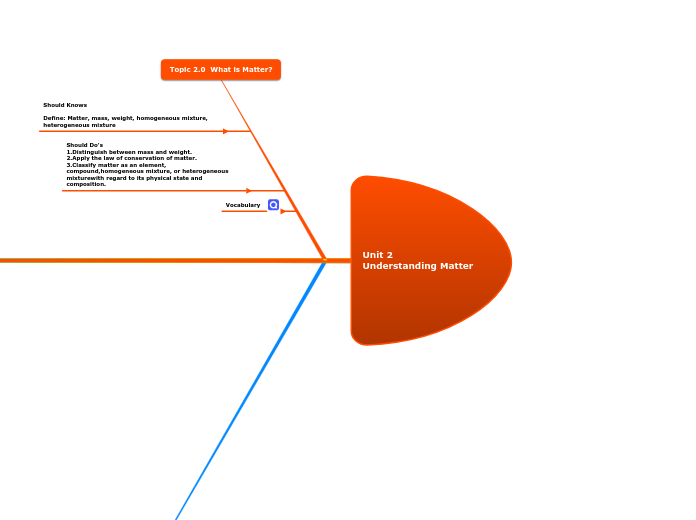
Unit 2 Ūnderstanding Matter
In the study of matter, several foundational concepts are critical. Matter itself is defined by its mass and occupies space, with distinctions made between mass and weight. Mass refers to the amount of matter in an object, while weight is the force exerted by gravity on that object.