jonka Letitia Looi 4 vuotta sitten
336
09_M1
jonka Letitia Looi 4 vuotta sitten
336

Lisää tämän kaltaisia
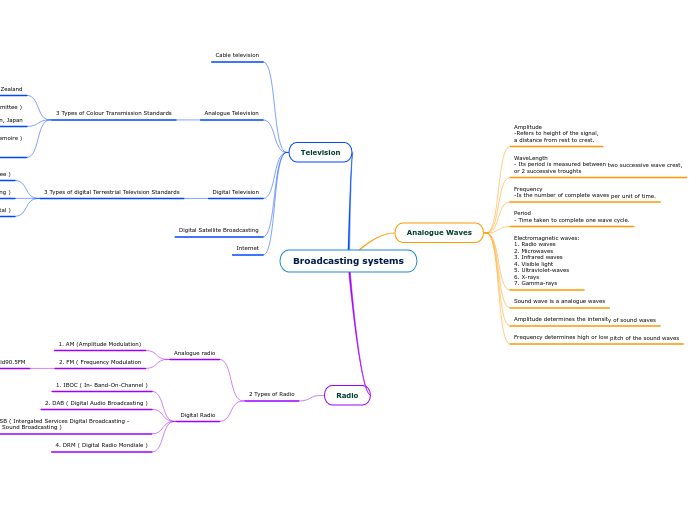
4. DRM ( Digital Radio Mondiale )
3. ISDB-TSB ( Intergated Services Digital Broadcasting - Terrestrial Sound Broadcasting )
2. DAB ( Digital Audio Broadcasting )
1. IBOC ( In- Band-On-Channel )
2. FM ( Frequency Modulation
E.g Class95FM, 98.7FM, Gold90.5FM
1. AM (Amplitude Modulation)
ISDB-T (Integrated Services Digital )
DVB ( Digital Video Broadcasting )
ATSC ( Advanced Television Systems Committee )
SECAM ( Sequential Couleur avec Memoire ) Countries like: etc. Syria, Benin.
NTSC ( National Television System Committee ) Counteries like: etc. North America, South Korea, Taiwan, Japan
PAL ( Phase Alternating Line ) Countries like: etc. Australia, China, India, New Zealand