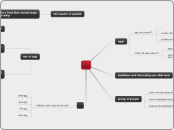
Experiments
Meselson and Stahl
Dispersive Model
Each strand of daughter and parent molecule has a mix of old and new DNA
Semiconservative Model
Two strands of parental molecule separate and each function as a template for new strand.
Proved to be the accurate model for DNA
Conservative Model
Two parental strands reassociate after acting as templates for new strands, which restores the parental double helix
Griffith
studied two different strains of the bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae
The R (Rough Strain)
Non Pathogenic because cells do not have a capsule
Living R Cells (Non Path Control) mouse lived
The S (smooth) Strain
Pathogenic because Cells have a smooth outer capsule
Mixture of R cells and heat killed S Cells killed the mouse
The R had been transformed into pathogenic S bacteria
Living S Cells (Pathogenic Control) killed mouse
Heat Killed S Cells (non path control) mouse lived
Hershey and Chase
Phages were grown with radioactive phosphorus and DNA was dyed blue
Phages was found in pellet rather then liquid which proved that DNA was the genetic material
Phages were grown with radioactive Sulfur and protein was dyed pink
Phage was found in liquid rather then pellet which proved protein was not the genetic material
Miller Urey
Set up a closed experiment to mimic conditions of primidal atmosphere
Found: Formaldehyde and Hydrogen Cyanide and other complex molecules such as amino acids and long chains of carbons and hydrogen also known as hydrocarbons
Trans-membrane protein, channel proteins, ion gated, and carrier proteins: found on the cell membrane to allow the transport of certain molecules into and out of the cell
Ion Gated Channels
These channels allow for the entering and existing of ions into and out of the cell. Example: K+/N+ Pump
Nerve cells send out neurotransmitters when the membrane potential reaches the highest capacity called action potential, neurotransmitters then act like signaling molecules passing through the synaptic cliff and binding to gated ion channels and opening them so that the neuron can respond.
The cell has a negative concentration compare to the outside of the cell. There is more K+ inside the cell and more N+ outside of the cell. The cell take in 2 K+ and 3 N+ out to stabliize the cell.
G Protein Receptor and Tyrosine Kinase Receptor
Signaling Molecules bind to the receptors and activates
When two signaling molecules bind to the Tyrosine Kinase Receptor the tyrosines dimerize and through phosphorylation 6 ATP is converted into 6 ADP and 6 P, the 6 phophasete groups bind to the 6 tyrosines activating the tyrosin Kinase Receptor
G Protein: Binds to the G protein receptor and change shape, removing GDP and adding GTP which makes the protein active
The active G protein then goes and activates a near by enzyme. Example: Adenylyl Cyclase
Adenylyl Cyclase convertes ATP into cAMP which is a secondary messenger.
cAMP then activates Protein Kinase A which through phosphorylation activates another Kinases and cascade until the last protein acceptor. PHOSPHORYLATION CASCADE
Last protein acceptor then sends the signal to organelles in the cytoplasm
The last protein goes into the nucleolus and and activates transcription factors to start the transcription complex and let RNA Poly make protein OR gene to be expressed
Gene Regulation
Prokaryotic
Prokaryotic cells have gene regulation sequences called operon where it contains operator and promoter for activators or repressor to bind to to allow RNA Poly to start transcription.
Eukaryotic
Eukaryotic Cells have gene regulation at two control elements: Distal control element and Proximal control element, where there are DNA sequence called enhancer where activators or repressors can bind to to start or inhibit the transcription initiation complex.
Introductory biology is the study of biomolecules and cellular components that work together to enable the translation of proteins that are the building blocks of living organisms. Through the idea of central dogma and regulation processes that make sure every step of a process is done correctly so that mutation cannot occur, living organisms can produce and live a healthier life.
Cell Membrane
The strucure of the cell membrane gives the membrane a function that allows certain molecules to enter the cell, while others to exits.
Lipids: Phospholipid- hydrophobic tails and hydrophilic head makings the membrane fluid.
Carbohydrate- cell to cell recognition.
Proteins: Cellular transportation
Fluid Mosaic: Cholesterol- Give the membrane more fluidity. The cell membrane is both saturated and unsaturated which during temperature change adjusts to make the cell more fluid.
Organelles
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Rough ER
it also grows in place by adding membrane proteins and phospholipids to its own membrane
most secretory proteins are knowns as glycoproteins, proteins with carbohydrates that are covalently bonded
has ribosomes on outer surface
Smooth ER
lacks ribosomes
important in synthesis of lipids, oils, and steroids and detox of drugs and poisons
common and important in liver cells
Lysosomes
a membrane sac that contains enzymes to digest macromolecules
Phagocytosis or "cell eating"
Nucleus
contains most genes of the cell and chromosomes
Nuclear Lamina
a netlike array of protein filaments that maintain shape of the nucleus
lines the envelope
Nuclear Envelope
is double membraned
encloses the nucleus separating its contents from the cytoplasm
Plasma Membrane
Selectively permeable membranes
functions as a selective barrier that allows passage enough oxygen, nutrients, and wastes to service the cell
Golgi
the transporter of the cell
Mitochondria
produces ATP through cellular respiration
Ribosomes
complexes made of RNA's and proteins are cellular components
Bound Ribosomes
are attached to the outside of the ER
Free Ribosomes
are suspended in the cytosol
Water properties
Denser as a liquid then as a Solid
Denser as a liquid at 3.98°C then when it freezes at 0 degree
Expansion Upon freezing
moderate temperature
Water can moderate temperature because of the two properties: high-specific heat and the high heat of vaporization
High heat of vaporization
High Specific heat
Cohesive behavior
water molecules are attracted to other water molecules
Universal solvent
dissolves more substances than any other solvent
Chemical Bonds
Van Der Waal Interactions
The weakest chemical bond that results from the shifting of electron inside the atom
Example: interactions Between Electrons of Iodide
Hydrogen Bonding
A special kind of covalent interaction that result in the bonding of hydrogen and other more electronegative elements
Example: Bond between Hydrogen and oxygen in H2O
Highly electronegative elements that can partake in hydrogen bonding: Hydrogen Nitrogen, Oxygen, Fluorine
Covalent Bonding
Interaction that result from the sharing of electrons
Example: Bond between Carbon and Oxygen in CO
Ionic Bonding
Interaction between two activity charged molecules
Example: Bond between K+ and I-
Biological Molecules
Nucleic acids
Used to make genetic material such as DNA and mRNA
macromolecules formed of nucleotides (polymers)
Held together through phosphodiester bonds
nucleotides are the monomers
carbohydrates
Used to make both complex and simple sugars which are used for energy
Macromolecules formed of monosaccharides (polymers)
Held together through glycosidic linkage
monosaccharides are the monomers
Triglycerides
Used to make Hormones such as steroids and hormones
Macromolecules formed by fatty acids (polymers)
Held together through Ester bonds
Fatty acids are the monomers
Proteins
Most common molecule used make most of the physical structures in the body
Macromolecules formed by amino acids (polymers)
Held together through peptide bonds
Amino acids are the monomers
Cell Communication
Signaling Molecules travel throughout our body: Local signaling, Long distance signaling, cell to cell communication, physical contact and chemical contact.
Lagging Strand
DNA pol 3 must work in the opposite direction of the fork to keep up with the other complementary strand, this requires multiple primers and it is made discontinuously
Central Dogma
Translation
ribosomal RNA's
consists of a large subunit and a small subunit, each made up of proteins
aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases
correct matching up of tRNA and amino acids is carried out by family of related enzymes
Anticodon
the loop extending from the other end of the L includes
tRNA
translates the message in a series of codons along an mRNA molecule
Transcription
Spliceosomes
a complex made of of protein and small RNA that remove introns
Exons
the other regions are later translated into amino acids
DNA Replication
Okazaki Fragments
segments that are left by the lagging strand
Ligase
joins all okazaki fragments into a contiunous DNA strand
Leading Strand
this only requires one primer for DNA pol 3 to synthesize
elongates the new DNA strand in the 5' to 3' end
DNA Polymerase
DNA Pol 3
adds DNA nucleotides to the RNA primer and continues to add DNA nucleotides complementary to the parental strands
DNA Pol 1
catalyzes the synthesis of new DNA by adding nucleotides to the 3' end of a pre existing chain
Primase
starts a complementary RNA chain with a single RNA nucleotide one at a time using the parental DNA strand as a template
Primer
the initial nucleotide chain produced during DNA synthesis that is made up of RNA
Topoisomerase
an enzyme that helps relieve the tension that was caused breaking, untwisting, and rejoining the DNA strands
Single-Stranded Binding Protein
binds to the unpaired strand so they do not pair themselves together
Replication Fork
found on both ends of the replication bubble and open in opposite directions
the "Y' shaped region where parental strands are being unwounded
Origin of Replication
Replication of DNA begins here
Needed in order to begin replication
Introns
non coding segments of nucleic acid that lie between coding region
RNA Splicing
remarkable of stage of RNA processing in the eukaryotic nucleus
RNA Processing
RNA Processing both ends of primary transcript are altered
TATA Box
the promoter sequence in DNA in forming the initiation complex at a eukaryotic promoter
Transcription Initiation Complex
complex of transcription and RNA pol pol 2 bound to the primer
Transcription Factors
a collection of proteins that mediate the binding of RNA pol and initiate transcription
Transcription Unit
the stretch of DNA downstream from the promoter that is transcribed into an RNA molecule
Terminator
the sequence that signals the end of transcription
Promoter
this allows RNA Pol to attach itself and initiates transcription
RNA Polymerase
pulls away two strands of DNA apart from each other and joins together RNA nucleotides complementary to the DNA template strand