jonka Hector Rodriguez 5 vuotta sitten
442
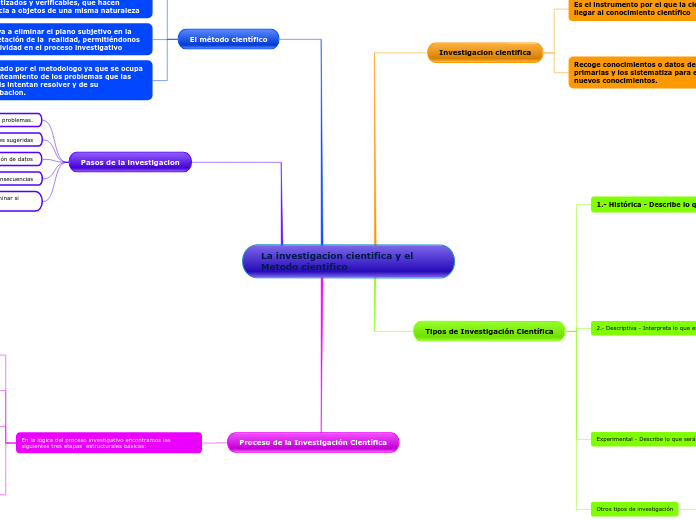
La investigacion cientifica y el Metodo cientifico
jonka Hector Rodriguez 5 vuotta sitten
442

Lisää tämän kaltaisia
In linguistics, syntax is the set of rules, principles, and processes that govern the structure of sentences in a given language, usually including word order.
A compound sentence is a sentence that has at least two independent clauses joined by a comma, semicolon or conjunction. An independent clause is a clause that has a subject and verb and forms a complete thought.
When independent clauses are joined with coordinators (also called coordinating conjunctions), commas and semicolons, they do more than just join the clauses. They add meaning and flow to your writing.
El ensayo cuidadoso de las conclusiones para determinar si encajan con las hipótesis formuladas
La recopilación, organización y valoración de datos.
La formulación de hipótesis o soluciones sugeridas.
La definición y redefinición de problemas
En esta etapa recibe el reconocimiento a su esfuerzo y, lo que es para él aún más importante, de la comunidad científica, que le es clave para continuar investigando
Cuando se sabe qué hacer y cómo hacerlo, entra en la etapa del raciocinio o del trabajo de campo y de laboratorio es la etapa de la consecución, interpretación y análisis de la información
Quien se dedica a formular el proyecto elabora un documento en el cual se especifican los aspectos tecnicos y administrativos que se requieren para la investigacion.
A complex sentence is a sentence that contains an independent clause and one or more dependent clauses.
An independent clause can stand alone as a sentence, but a dependent clause even though it has a subject and a verb cannot stand alone.
Attributive clauses serve as an attribute to a noun (pronoun) in the main clause. This noun or pronoun is called the antecedent of the clause.
An adverbial clause is a group of two or more words that function as an adverb in a sentence.
An appositive clause follows another noun or noun phrase in apposition to it; that is, it provides information that further identifies or defines it.
See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences.
Tim is driving the red car.
See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences.
Tim is the driver.
cuasiexperimentales
experimentales
preexperimentales
See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences.
Tim drives the car.
B) Muestra
6. Categorías de datos, a fin de facilitar relaciones. 7. Verificación de validez de instrumentos. 8. Descripción, análisis e interpretación de datos.
A) Población
1. Descripción del problema. 2. Definición y formulación de hipótesis. 3. Supuestos en que se basan las hipótesis. 4. Marco teórico. 5. Selección de técnicas de recolección de datos.
See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences.
Tim drives.
5. Interpretación e informe
4. Formulación de hipótesis
3. Crítica de las fuentes
2. Recolección del material informativo
1. Enunciación del problema
The predicate of a sentence is the part that modifies the subject in some way. Because the subject is the person, place, or thing that a sentence is about, the predicate must contain a verb explaining what the subject does and can also include a modifier.
3.- Crear instrumentos si no estan creados
2.- Recoger, registar y analizar los datos obtenidos
1.- Planear una metodologia
The subject of a sentence is the person, place, thing, or idea that is doing or being something. You can find the subject of a sentence if you can find the verb.
Ask the question, 'Who or what 'verbs' or 'verbed'?' and the answer to that question is the subject.