jonka Susana García 4 vuotta sitten
238
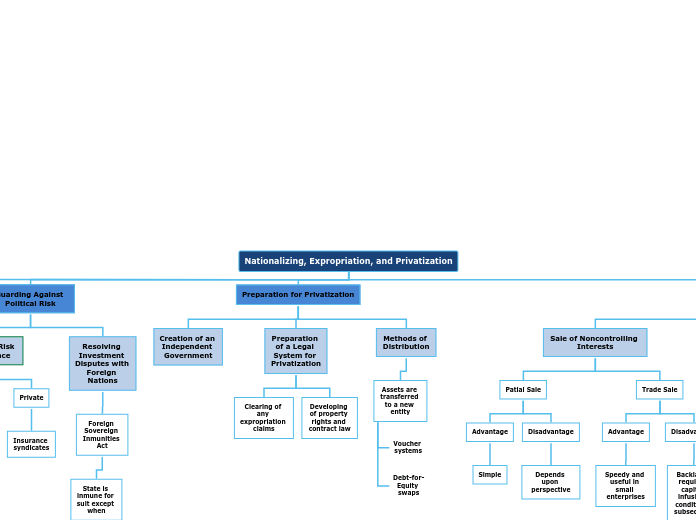
Nationalizing, Expropriation, and Privatization
jonka Susana García 4 vuotta sitten
238

Lisää tämän kaltaisia
Mix of trade sale and non-controlling interest model
Shareholder Agreement
Build-Operate-Own
Build-Operate-Transfer
Management are owners, layoffs difficult
Gives government employees a stake in the outcome, may bring in labor unions
Backlash, requires capital infusion, conditions subsequent
Speedy and useful in small enterprises
Disadvantage
Depends upon perspective
Advantage
Simple
Debt-for-Equity swaps
Voucher systems
State is inmune for suit except when
Noncommercial torts
Commercial activity
Waiver
Insurance syndicates
MIGA
OPIC
Expropriation
taking a single company
Nationalization
taking an entire industry