jonka SC - 12KS 1014490 Sandalwood Heights SS 2 vuotta sitten
214
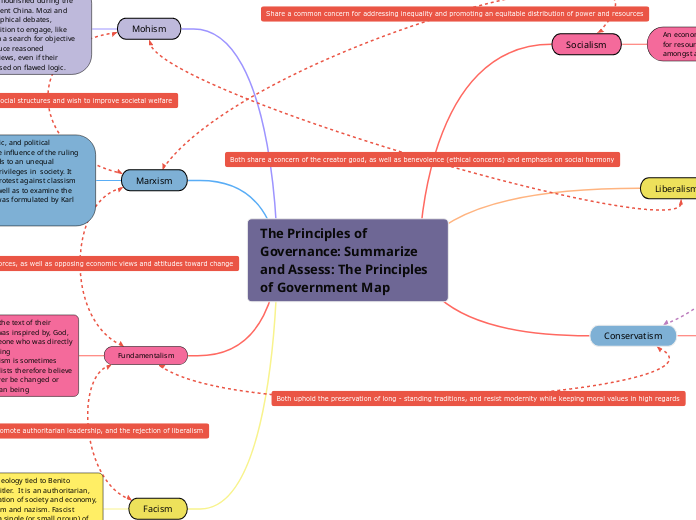
The Principles of Governance: Summarize and Assess: The Principles of Government Map
jonka SC - 12KS 1014490 Sandalwood Heights SS 2 vuotta sitten
214

Lisää tämän kaltaisia