jonka Tung Wai Kiong Derek (Mr) N/A 10 vuotta sitten
6224
Transport
jonka Tung Wai Kiong Derek (Mr) N/A 10 vuotta sitten
6224

Lisää tämän kaltaisia
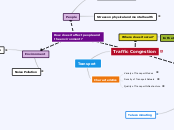
Ways to manage the number of cars on the road.
Road Pricing = charges drivers when they use certain roads.
Drivers required to pay more during peak hours to discourage the usage of certain roads.
Eg. Electronic Road Pricing (ERP) in Singapore
Eg. Stockholm Congestion Tax in Sweden.
Increased parking fees would increase the cost of driving especially to and from the CBD.
This would encourage people to take public transport.
It would also encourage people to carpool. (group of people travelling together in one car and sharing the cost)
Use of technology to monitor traffic. It can alert drivers of traffic congestion so that they can avoid travelling on that road.
Eg. Expressway Monitoring and Advisory System (EMAS) in Singapore. (Live information made available to drivers)
Eg. Green Link Determining System (GLIDE) in Singapore. (computerised traffic light signalling system which detects volume of traffic on the roads the adjust the green time according to traffic conditions.)
Physical health = condition of a person's body.
Mental health = person's psychological state indicated by his/her emotions and behaviour.
Long travelling times = fatigue = losing concentration = accidents/deaths. (Physical)
Exhaust fumes can cause illnesses such as asthma and lung diseases. (Physical)
More time spent on roads = stress and frustration = more prone to accidents/fights (Mental)
Productivity = rate at which good or services are produced.
Traffic congestion reduces productivity because people have to spend more time commuting which results in time wasted that can be used on productive work.
This leads to economic losses for the country as a whole.
People may need to move about within the city to obtain goods and services. (Eg. Purchasing goods from stores / attending classes)
People may also need to move about within the city to provide goods and services. (Eg. wholesalers deliver to retails shops and home delivery services delivery products to homes.)
The delivery of good is done through freight trucks and motorcycles. Movement of these vehicles within the city may lead to traffic congestion.
Noise pollution occurs when there is harmful and excessive noise that may disrupt human and animal life.
Noise pollution from drivers honking their cars frequently. Prolonged exposure to harmful noises can trigger heart disease, high blood pressure and mental illness.
Cars emit greenhouse gases. (Eg. Carbon Dioxide/Carbon Monoxide)
These gases traps heat and cause earth's temperature to rise.
Constant acceleration and braking motion in a traffic congestion increases emission of greenhouses gasses.
Smog = smoke and fog from car exhaust and particles from cars and factories.
Can cause difficulty breathing, asthma, colds and eye irritation.
Improving public transport system by making it more convenient and accessible. This would encourage people to take public transportation.
Upgrading of bus and rail systems to carry more people and arrive more frequently.
Eg. Singapore - Bus Service Enhancement Programme in 2012. (Reduce waiting times for buses)
Eg. Singapore - Land Transport Master Plan - increase capacity and frequency of trains, upgrading of train signalling system.
Expansion of rail networks = trains can reach more locations.
Can be done in two ways:
1)More tracks can be laid so that rail network covers a larger area.
2)More stations can be built so that more locations have access to trains.
Bus lanes = lanes set aside for private and public buses on specific days and times.
Helps buses enter and exit bus stops smoothly and quickly therefore improving bus speeds and reliability.
Integrated Public Transport System = a public transportation system that is seen as a whole regardless of the modes of transport.
Eg. Japan: all public transport modes can be paid by the same smart card.
Eg. Singapore: transport hubs with bus terminals that are integrated with rail and retail services. Same ticketing system. (EZ-Link)
People often work and live in different parts of the city resulting the need for people to commute.
This can be done via public or private transportation by people prefer to use private transportation because it is convenient and flexible.
Therefore, the high volume of cars that drive in and out of the CBD result in traffic congestion.
Bicycles = environmentally friendly, convenient and flexible.
Eg. Copenhagen in Denmark. (Wide cycling lanes, bicycle parking lots in the city)
More people cycling, less cars on the road = less traffic congestion.
Telecommuting = work arrangement where employees work from home or at a location near their home and therefore do not need to travel to the office. (reduces vehicles on the road = less traffic congestion)
Made possible by technology. (Eg. internet connections, computers, telephone lines)
Able to communicate with colleagues or clients even when they are not physically in the office.
Inadequate transport infrastructure = transport facilities not capable of handling the amount of traffic it receives. (Eg. road not enough lanes, not well-connected)
Transport services = services provided to move people and goods from one location to another.
Poor provision = small fleet of public buses / trains. Does not arrive frequently or on time.
Therefore it forces people to avoid public transport and take private transportation instead. There will be more vehicles of the road leading to traffic congestion.
The central business district (CBD) is the commercial center where financial institutions and concentrated. Therefore it is the most concentrated and most well -connected.
Traffic congestion happens during peak hour. (Part of the day where traffic volume is the highest)
Transport infrastructure = facilities such as roads, railway tracks, bus terminals.
Characteristic of High Quality Transport Infrastructure:
1) Large Capacity - Able to move large numbers of people at any one time.
2) Efficient - Frequent services to move people around.
3) Comfortable - Clean travelling environment allows for a comfortable commute.
4) Dependable and reliable - Transport system can be depended upon to move people constantly, on time with few interruptions.
5) Safe - Little danger of accidents, presence of safety features such as track barriers and emergency buttons on trains.
Transport network = system of transport routes connecting a set of nodes.
Dense transport network = highly developed and well-connected. (Easier for people to get around the city)
Modes of transportation refers to the types of transport.
Private transport: transport owned by individuals (Eg. motorcycles / cars)
Public transport: transport provided by the government or private companies. (Eg. buses / trains / taxis)
Traffic Congestion is a situation where there are more vehicles than the road can handle.
Characteristics: slow travelling speeds, long vehicular queues.