Anaerobic and Aerobic cellular respiration (3.2-3.3)
Oxidative phosphorylation involves two events. The electron transport chain oxidizes NADH or FADH2 and generates an H1 gradient. This gradient is used by ATP synthase to make ATP via chemiosmosis.
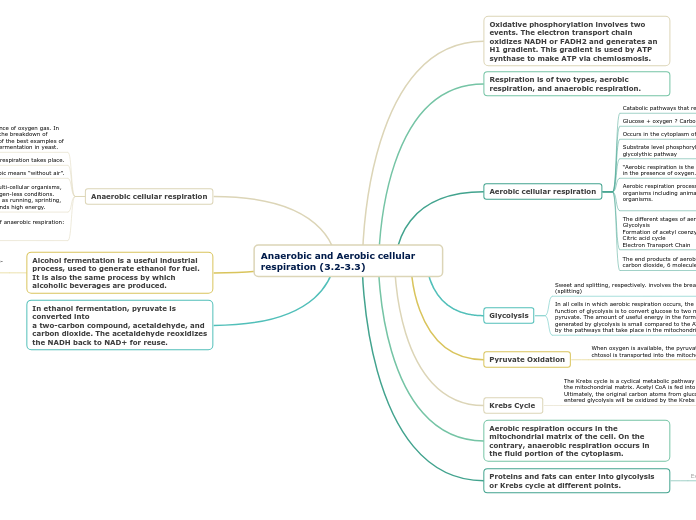
Respiration is of two types, aerobic respiration, and anaerobic respiration.
Aerobic cellular respiration
Catabolic pathways that require oxygen
Glucose + oxygen ? Carbon dioxide + water + ATP
Occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell, and in the mitochondrion
Substrate level phosphorylation; At various steps in the glycolythic pathway
“Aerobic respiration is the process of producing cellular energy in the presence of oxygen.”
Aerobic respiration process takes place in all multicellular organisms including animals, plants and other living organisms.
The different stages of aerobic respiration are:
Glycolysis
Formation of acetyl coenzyme A
Citric acid cycle
Electron Transport Chain
The end products of aerobic respiration include 6 molecules of carbon dioxide, 6 molecules of water and 30 molecules of ATP.
Example
Glycolysis
Sweet and splitting, respectively. involves the breakdown (splitting)
In all cells in which aerobic respiration occurs, the main function of glycolysis is to convert glucose to two molecules of pyruvate. The amount of useful energy in the form of ATP generated by glycolysis is small compared to the ATP produced by the pathways that take place in the mitochondria.
Pyruvate Oxidation
When oxygen is available, the pyruvate produced in the chtosol is transported into the mitochondrial matrix.
Krebs Cycle
The Krebs cycle is a cyclical metabolic pathway that occurs in the mitochondrial matrix. Acetyl CoA is fed into the pathway. Ultimately, the original carbon atoms from glucose that entered glycolysis will be oxidized by the Krebs cycle.
Aerobic respiration occurs in the mitochondrial matrix of the cell. On the contrary, anaerobic respiration occurs in the fluid portion of the cytoplasm.
Proteins and fats can enter into glycolysis or Krebs cycle at different points.
Example
Anaerobic cellular respiration
a process which takes place in the absence of oxygen gas. In this process, the energy is obtained by the breakdown of glucose in the absence of oxygen. One of the best examples of anaerobic respiration is the process of fermentation in yeast.
Oxygen is absent when this form of respiration takes place.
Anaerobic means “without air”.
Anaerobic respiration is also used by multi-cellular organisms, like us, as a temporary response to oxygen-less conditions. During heavy or intensive exercise such as running, sprinting, cycling or weight lifting, our body demands high energy.
Example
There are two main types of anaerobic respiration:
Alcoholic fermentation
Lactic acid fermentation.
Example
Alcohol fermentation is a useful industrial process, used to generate ethanol for fuel. It is also the same process by which alcoholic beverages are produced.
In lactate fermentation, pyruvate oxidizes NADH back to NAD+ and, in the process, is converted into lactate. In single-celled organisms, the lactate is released to the