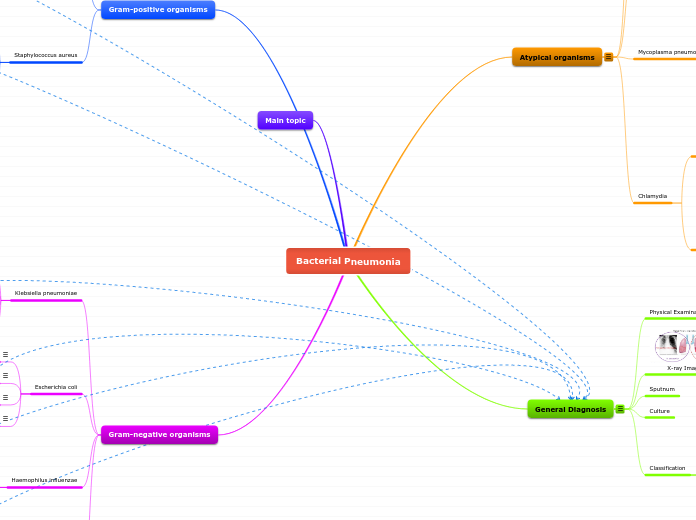
Bacterial Pneumonia
Gram-positive organisms
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Virulence Factors 1
General Characteristics 1
Diagnosis 1
Treatment 1
Staphylococcus aureus
Virulence Factors 2
General Characteristics 2
Diagnosis 2
Treatment 2
Main topic
Gram-negative organisms
Klebsiella pneumoniae
Virulence Factors 3
General Characteristics 3
Diagnosis 3
Treatment 3
Escherichia coli
Virulence Factors 4
General Characteristics 4
Diagnosis 4
Treatment 4
Haemophilus influenzae
Virulence Factors 5
General Characteristics 5
Diagnosis 5
Treatment 5
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Virulence Factors 6
General Characteristics 6
Diagnosis 6
Treatment 6
Atypical organisms
Legionella pneumophila
Virulence Factors 7
General Characteristics 7
Diagnosis 7
Treatment 7
Coxiella burnetti
Virulence Factors 8
General Characteristics 8
Diagnosis 8
Treatment 8
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Virulence Factors 9
General Characteristics 9
Diagnosis 9
Treatment 9
Chlamydia
Chlamydia psittaci
Virulence Factors 10
Diagnosis 10
General Characteristics 10
Treatment 10
Chlamydophila pneumoniae
Treatment 11
General Characteristics 11
Diagnosis 11
Virulence Factors 11
General Diagnosis
Physical Examinations
X-ray Imaging
Lobar
Bronchopneumonia
Sputnum
Culture
Classification
Lobar
Bronchopneumonia
Lobular
Interstitial