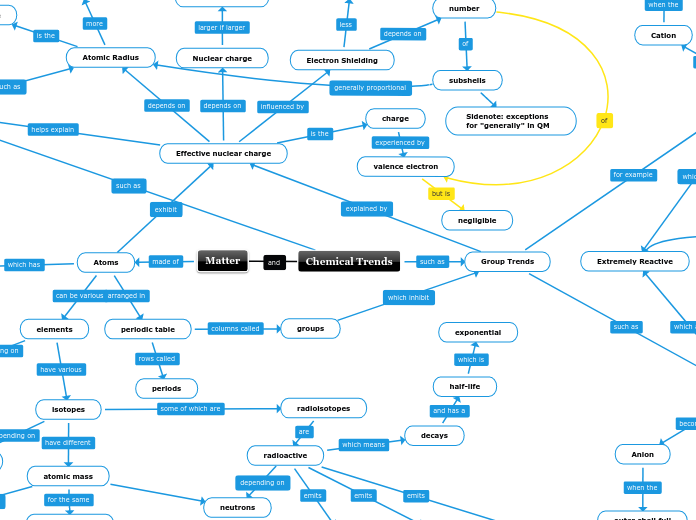
Chemical Trends
Group Trends
Group 1
Alkali Metals
Metals
More reactive
Cation
outer shell full
Group 17
Halogens
Non metals
Extremely Reactive
More reactive
1 Electron
Stable shell
Anion
outer shell full
Matter
Atoms
Atomic Structure
Simplified models
properties, trends, etc
Conceptualization
diagrams
Quantum Model
Proton
positively charged
+1
elementary charge
smallest possible charge
Neutron
nucleus
centered in atom
no charge
Electron
-1
clouds of uncertainty
heisenberg uncertainty principle
position
same time
momentum
shells
subshells
sphere
dumbbell
cloverleaf
elements
proton count
isotopes
neutron count
radioisotopes
radioactive
decays
half-life
exponential
alpha radiation
beta radiation
gamma radiation
atomic mass
neutrons
same element
periodic table
groups
periods
Effective nuclear charge
Nuclear charge
Atomic Number
Protons
electrons
Coulomb's Law
Electron Shielding
ENC
more electrons
number
subshells
Sidenote: exceptions for "generally" in QM
Atomic Radius
ENC
closer
distance
nucleus
small
picometer
across the period
down the group
charge
valence electron
negligible
Trends
Electron Affinity
period
electron is attached
Electronegativity
period
group
tendency to attract
electrons
bond
Ionisation Energy
energy
an electron
atomic number
increases
Heat+Light
Water
Acid
Hydrogen gas + Base
Bohr Rutherford
shells
spherical
Da
1/12 mass
Carbon 12 atom