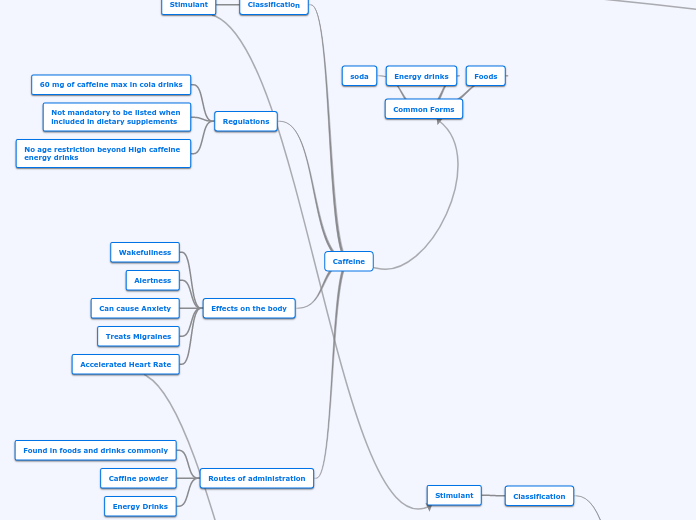
Caffeine
Classification
Stimulant
Regulations
60 mg of caffeine max in cola drinks
Not mandatory to be listed when
included in dietary supplements
No age restriction beyond High caffeine
energy drinks
Effects on the body
Wakefullness
Alertness
Can cause Anxiety
Treats Migraines
Accelerated Heart Rate
Routes of administration
Found in foods and drinks commonly
Caffine powder
Energy Drinks
Tobacco
Common forms
Cigarettes
JUUL
Chew
Nicorette Gum
Swishers
Regulations
Regulated by FDA
as of 2009
Age 18 or 21 depending by state
21 in Oregon
18 in Washington
How it Works
Brain
Nicotine has positive working brain effects
Causes release of adrenaline
Dopamine release less
prominent than other drugs
Central Nervous System
Ups sugar production to fight appetite
Reinforces drug taking behavior
Produces psychoactive neurochemicals
Concerns
More addictive than heroin
80% of lung cancer cases are
previous smokers
COPD and Bronchitis
Classification
Stimulant
How its used
Smoked
Pipe
Rolled
Vaped
Chewing tobacco
Hookah
Gum/Patches
Snorted
Effects on The Body
Accelerated heart rate
Drop in blood pressure
Lightheaded
May improve memory
Loss of sense of smell and taste
Routes of Administration
Available to anyone of legal age in most stores
Common Forms
soda
Energy drinks
Foods
Methamphetamine
Routes of Administration
Smoked
Pipes
Injected
Snorted
Pill or ingested
Classification
Stimulant
Mainly Effects Brain
Effects CNS
Effects on the Body
Intense inital rush
Euphoria
Increased energy and alertness
Can last 12 Hours
Common Forms
Crack
Crystal Meth
Meth Tablets
Liquid Meth
Regulations
Concerns
Insomnia
Paranoia
Violent outbursts
How it Works
Brain
Triggers dopamine release
Not recycled
Craved to prevent crash
Effects serotonin neurons
Central Nervous System
Increased Neuron Death
Decreased white matter
Produces Neurochemicals
How its Used
USed to aid weightloss
MOstly used illegally
Smoked
Snorted
Intravenously
Schedule II Drug
Enforced by DEA
Outlawed in 1983
Addictive
More criminalized than Cocaine
Confusion
Anxity
Alpharolam
Common forms
Xanax
Regulations
Schedule IV
Mild risk for dependence
Available by prescription only
How it Works
Binds to GABA Recptor
Produces
Slows Brain Activity
GABA is natural tranquilizer
Breaches Brain body barrier
Concerns
Dangerous when mixed with alcohol
Easy to O.D.
Memory damage
Increased suicidal thoughts
Serious withdrawal
How its Used
Taken as a pill
Snorted
Effects on Body
Causes Calm Feeling
Stops Anxiety
Early effects similar to alcohol
Depresses CNS
Routes of administration
TAken as pill
Less than 6 mg. per day
Broken up and snorted