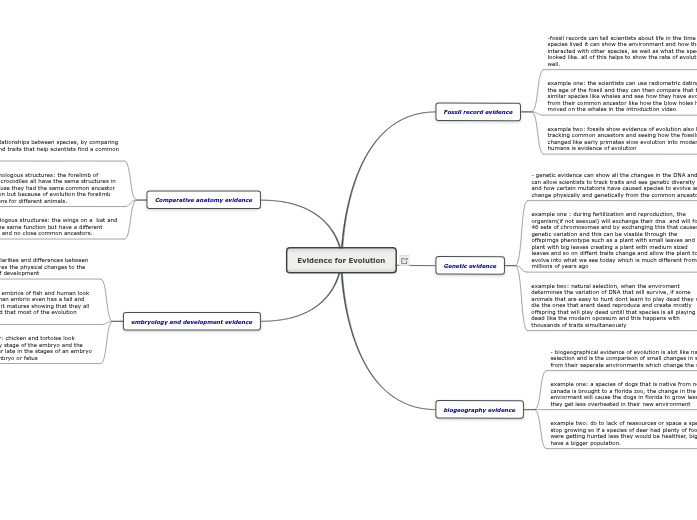
Evidence for Evolution
Fossil record evidence
-fossil records can tell scientists about life in the time certain species lived it can show the environment and how the species interacted with other species, as well as what the species looked like. all of this helps to show the rate of evolution as well.
example one: the scientists can use radiometric dating to find the age of the fossil and they can then compare that to other similar species like whales and see how they have evolved from their common ancestor like how the blow holes had moved on the whales in the introduction video
example two: fossils show evidence of evolution also by tracking common ancestors and seeing how the fossils have changed like early primates slow evolution into modern humans is evidence of evolution
Genetic evidence
- genetic evidence can show all the changes in the DNA and can allow scientists to track traits and see genetic diversity and how certain mutations have caused species to evolve and change physically and genetically from the common ancestor
example one : during fertilization and reproduction, the organism(if not asexual) will exchange their dna and will form 46 sets of chromosomes and by exchanging this that causes genetic variation and this can be visable through the offspirngs phenotype such as a plant with small leaves and a plant with big leaves creating a plant with medium sized leaves and so on diffent traits change and allow the plant to evolve into what we see today which is much different from millions of years ago
example two: natural selection, when the enviroment determines the variation of DNA that will survive, if some animals that are easy to hunt dont learn to play dead they will die the ones that arent dead reproduce and create mostly offspring that will play dead untill that species is all playing dead like the modern opossum and this happens with thousands of traits simultaneously
biogeography evidence
- biogeographical evidence of evolution is alot like natural selection and is the comparison of small changes in species from their seperate environments which change the species
example one: a species of dogs that is native from northern canada is brought to a florida zoo, the change in the enviorment will cause the dogs in florida to grow less fur, so they get less overheated in their new environment
example two: do to lack of reasources or space a species may stop growing so if a species of deer had plenty of food and were getting hunted less they would be healthier, bigger and have a bigger population.
Comparative anatomy evidence
-helps determine relationships between species, by comparing similar structures and traits that help scientists find a common ancestor.
example one of homologous structures: the forelimb of humans, birds and crocodiles all have the same structures in their forelimbs because they had the same common ancestor way back in evolution but because of evolution the forelimb has different functions for different animals.
example two of analogous structures: the wings on a bat and an insect perform the same function but have a different evolutionary origins and no close common ancestors.
embryology and development evidence
_embryology shows the similarities and differences between different species and compares the physical changes to the embryo in different stages of development
example of embryology: the embrios of fish and human look almost identical and the human embrio even has a tail and gills but is reabsorbed when it matures showing that they all came from one organism and that most of the evolution occurs in that stage
examples two of embryology: chicken and tortoise look virtually identical in the early stage of the embryo and the only really differences appear late in the stages of an embryo and mostly in the mature embryo or fetus