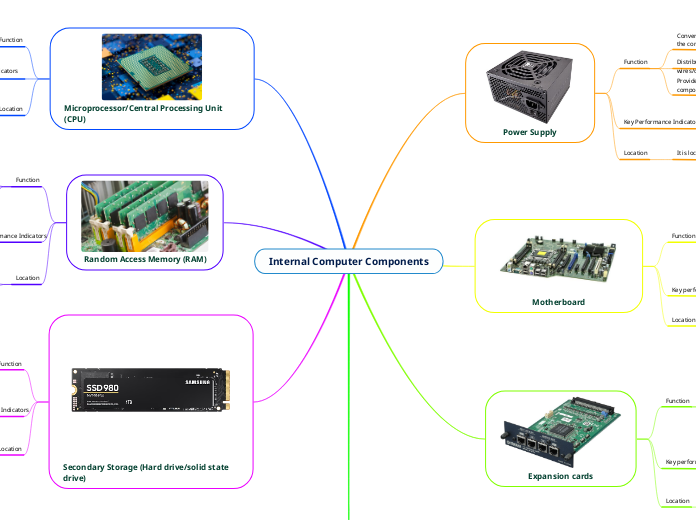
Internal Computer Components
Power Supply
Function
Converts power from a wall plug to power that can be used by the computer.
Distribute power throughout the computer through wires/cables.
Provides fail-safes for misplaced currents and protect components during a PC crash.
Key Performance Indicators
Should have fail-safes built in.
Better PSUs generally have higher wattages.
Location
It is located at the back of the computer, usually at the top.
Motherboard
Function
A thin plate containing the computer's CPU, RAM, hard drive and optical drive connectors, expansion cards for controlling the video and audio, and connections to its ports.
Every component of the computer is connected to the motherboard either directly or indirectly.
Key performance indicators
More expensive motherboards generally have
higher quality components such as higher quality capacitors, better power regulation components, and the PCB may have more layers and be more robust.
Location
Inside the computer case - it is the biggest circuit board
Expansion cards
Function
Expansion cards are used to boost the performance of
a computer or to add functionality to older computers.
There are many different kinds of expansion cards. Some of
the most common are: video cards, sound cards, network cards, and bluetooth cards.
Key performance indicators
Expansion cards vary but generally good expansion cards are those with higher quality parts.
Compatibility is very important, as it must be compatible with the device to be installed.
Location
Plugs into the computers motherboard .
Sources
Microprocessor/Central Processing Unit (CPU)
Function
Control center of the computer - contains all the circuitry needed to process input and output results.
A CPU's performance is measured in megahertz (MHz) - millions of instructions per second - or gigahertz (GHz) - billions of instructions per second - the more instructions per second the better the CPU.
Location
Inside the computer case in the motherboard.
Fits into the motherboard's CPU socket.
Random Access Memory (RAM)
Function
Temporary storage of memory so that it can easily accessed instead of going into long-term storage in the hard drive.
Ram is wiped when your computer is turned off.
Used for processes, apps, and programs that are currently running on your computer.
Key Performance Indicators
Memory speed and memory capacity are the two indicators of good RAM.
Location
Ram is in the motherboard - specifically it is usually stored outside the CPU in separate chips.
Ram can be added on to some computers through available slots in the motherboard.
Secondary Storage (Hard drive/solid state drive)
Function
Stores software, documents, and other files.
The data stored stays intact when turning off the computer, unlike RAM.
Key Performance Indicators
A faster hard drive can start up and load programs faster.
Solid state drives are much faster that traditional hard drives and will likely fully phase them out soon.
Location
They are typically located in the drive bay and are connected to the motherboard using a cable in one of several different formats.