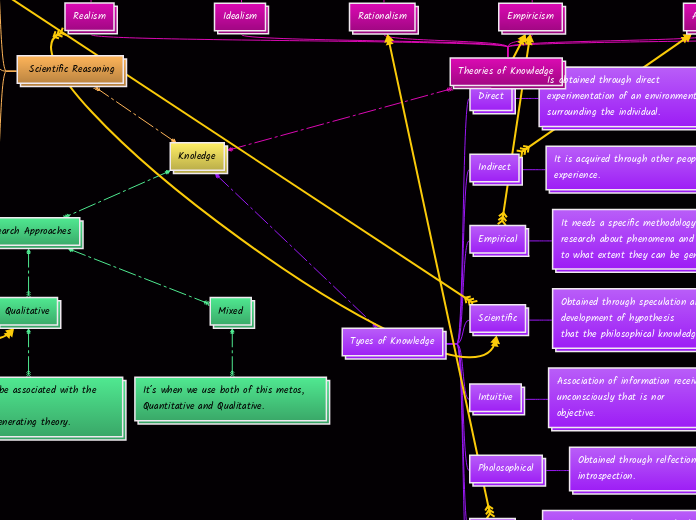
Knoledge
Scientific Reasoning
Scientific Method
This is a strategy used to try and explain natural science
rationally by observing and evaluating data.
Deductive Reasoning
The process of deducing is the formulation of a conclusion
based on generally accepted statements or facts. Specific
conclusions are drawn from general or universal premises.
Inductive Reasoning
This one involves an element of probability.
Generalizations are formed based on what you know or
observe.
Research Approaches
Quantitative
It is likely to be associated with a deductive approach
tot testing theory, often using numbers or facts.
Qualitative
It is likely to be associated with the inductive
approach to generating theory.
Mixed
It´s when we use both of this metos, Quantitative and Qualitative.
Tyoes of Knowledge
Direct
Is obtained through direct experimentation of an environment
surrounding the individual.
Indirect
It is acquired through other people’s experience.
Empirical
It needs a specific methodology to do research about phenomena and find out
to what extent they can be generalized.
Scientific
Obtained through speculation and the development of hypothesis
that the philosophical knowledge offers.
Intuitive
Association of information received unconsciously that is nor
objective.
Pholosophical
Obtained through relfection and introspection.
Logical
Conclusions are coherent with the premises that they are part of.
Religious
Based on dogma, faith, or beliefs.
Theories of Knowledge
Realism
Reality exists independent of
our thoughts or ideas, even
our consciousness.
Idealism
Reality is shaped by our
thoughts and ideas.
Rationalism
Reasoning and logics give
meaning to things.
Empiricism
Experiencig and
experimenting are the only
ways to acquire meaning.
Apriorism
Knowing something real without the need of experiencing it.
Intellectualism
Reflection occurs on ideas and real objects.