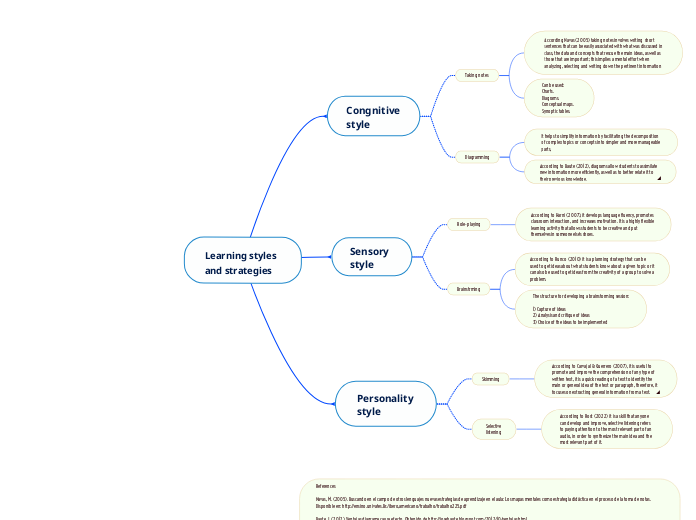
Learning styles and strategies
Congnitive style
Taking notes
Can be used:
Charts.
Diagrams.
Conceptual maps.
Synoptic tables.
Diagramming
Sensory style
Role-playing
Brainstrming
The structure for developing a brainstorming session:
1) Capture of ideas
2) Analysis and critique of ideas
3) Choice of the ideas to be implemented
Personality style
Skimming