MALIGN AND BENIGN PATHOLOGIES IN BREAST
MAIN FINDINGS

Mammary duct ectasia
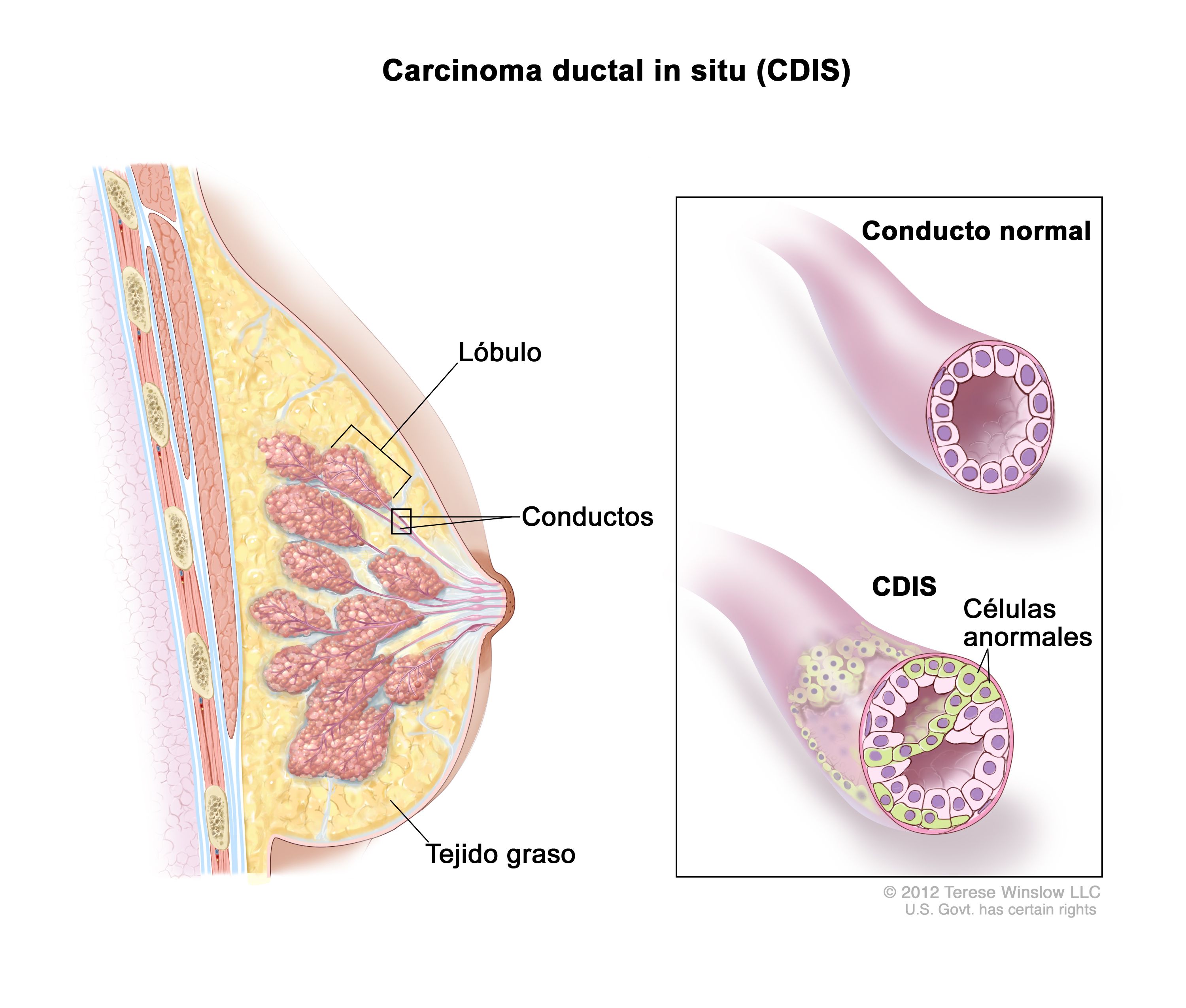
Intraductal papilloma
*Main cause of women who are not breastfeeding
*Bloody discharge
*Surgical removal of the duct

Purulent discharge from the nipple
*Infection
*Can produce an abcess
*Atibiotic treatment
Galactorrhea
*Involutive, bilateral, spontaneous, with pregnanciy and hipothyroidism

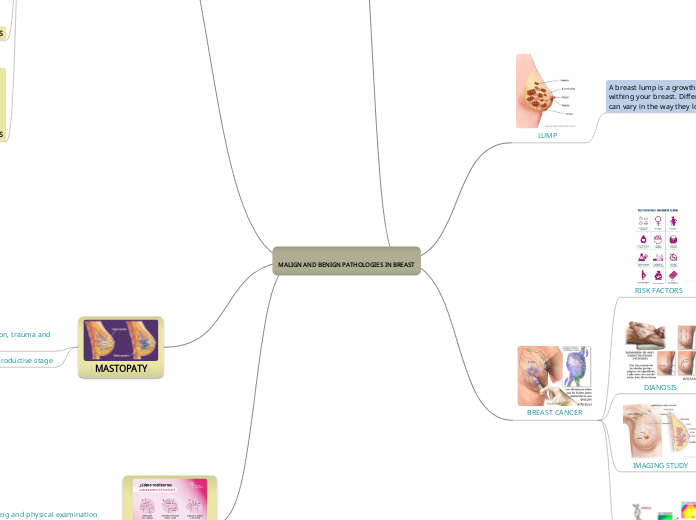
LUMP
A breast lump is a growth of tissue develops withing your breast. Different types of breast lumps can vary in the way they look and feel.
BREAST CANCER

RISK FACTORS
-Early menarche
-Family background
-Nulliparas
-Menopause
-Radiotherapy
-Ductal hyperplasia
-Age
-Use of exogenouse hormones
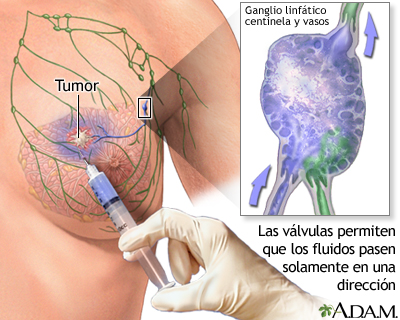
DIANOSIS
*Physical exam
*Self-exploraion
*Thorough questioning

IMAGING STUDY
*Biopsy
*Mammography
*Birads
*Ultrasound
*MRI

BIOLOGICAL MARKERS
*Estrogen receptors
*Progesterone
*Tumor size
p53
*HER2/neu
*Axillary lymph node status
BENIGN ALTERATIONS
GALACTOCELE
*Thick milky liquid
*Condensed
*Painful breast cyst

ADENOMA
-Scattered stroma
-Peak incidence at 20-30 years
-Circumscribed tumors

LIPOMA
*Most common non-epithelial neoplasm
*Fatty
*Mobile
*White tummor
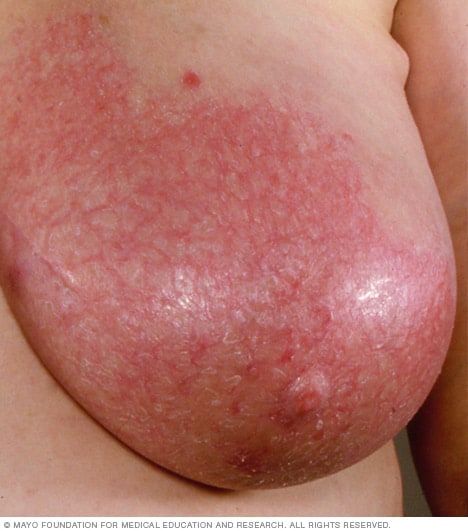
MASTITIS
- May appear in puerperal phenomena
-Sthapylococcus aureus
- Related to lactation factors
DUCTAL ECTASY
* Small abscess at the base of the nipple
*Perimenopause and postmenopause
*Hard and tender erythematous mass

Phylloid tumor
- Total surgical diagnosys
- Any age
Slow-growing epithelial neoplasia
PLOTIFERATIVE ALTERATIONS
*Hyperplasia
*Adenosis
*Seropurulent exudate
*Athypical dictated epithelium
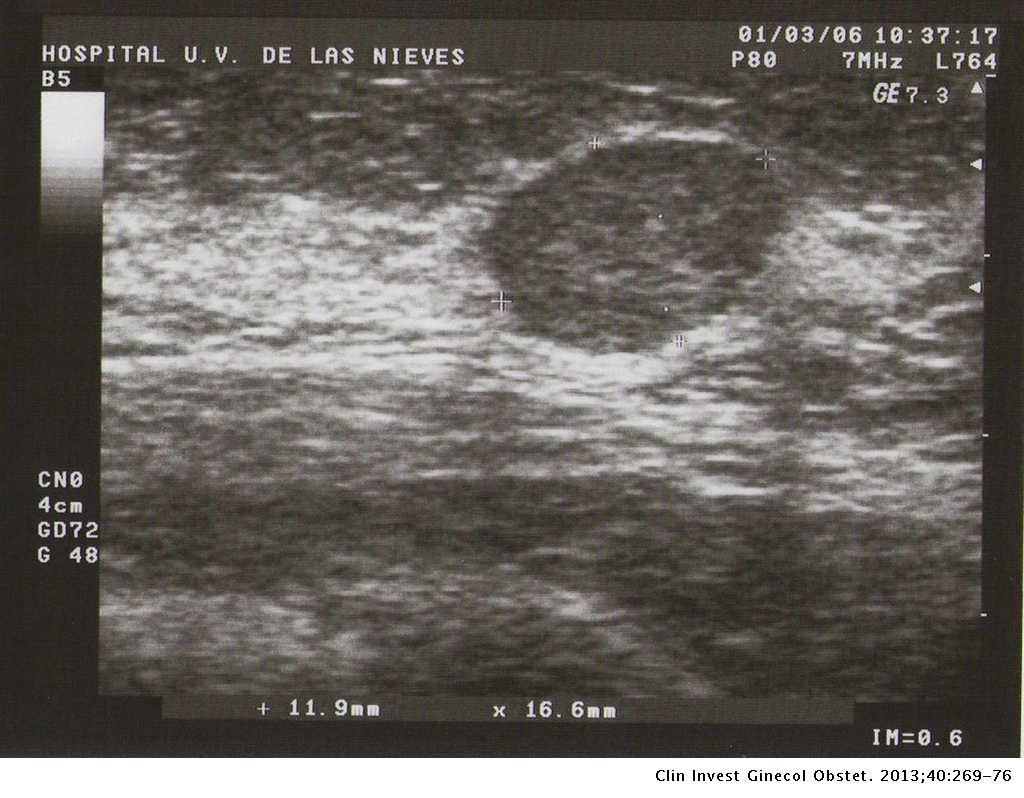
FIBROCYSTIC ALTERATIONS
-Edema
- Pain
-More common
-Premenopause
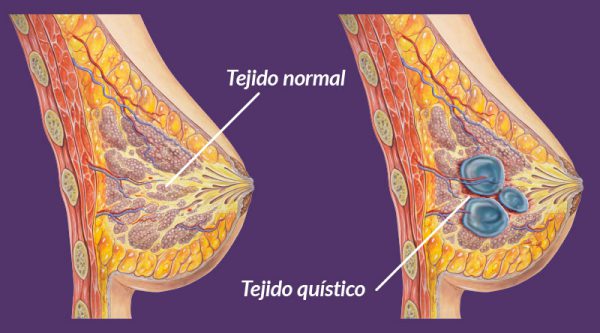
MASTOPATY
-Is associated with pregnancy, lctation, trauma and thrombophlebitis
-In reproductive stage

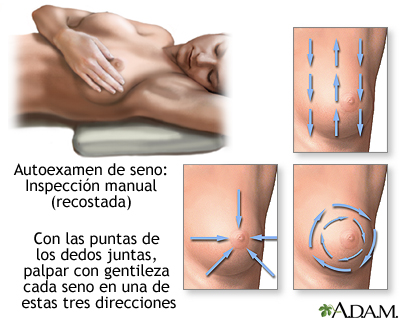
SELF-EXAMINATION
Questioning and physical examination
Palpation, inspection