Skeletal System
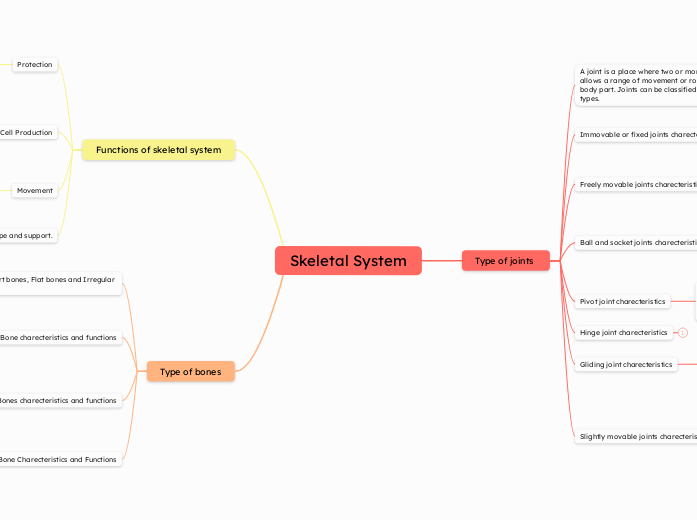
Functions of skeletal system
Protection
The skeleton protects vital organs such as the brain, heart and lungs.
For example, the cranium protects the brain, the ribs protect the heart and
lungs, the pelvis protects the abdomen, and the vertebrae protects the spinal cord.
Blood Cell Production
The bones produce blood.
Blood cells are made in the bone marrow of long bones such as the femur,
humerus and ribs.
The bone marrow of a human adult produces all of the red blood cells, some of the white cells, and all of the platelets in the body.
Movement
The skeleton allows the body to create movement.
Muscles are attached to bones.
The muscles contract and pull on the bones to create movement.
Shape and support.
The bones form a framework to support the body and give it shape.
The different lengths and thicknesses of the bones make up the unique size and shape of a body.
Type of joints
A joint is a place where two or more bones meet, it allows a range of movement or rotation for a body part. Joints can be classified into three main types.
Immovable or fixed joints charecteristics
They do not allow movement between the bones.
They are also known as fibrous joints because the bones are joined by fibrous connective tissue.
An example is the joints between the plates of the cranium.
Freely movable joints charecteristics
They can move freely.
They are also known as synovial joints.
Examples: the shoulder, elbow, hip, knee and ankle joints.
Ball and socket joints charecteristics
The round end of one bone fits into the hollow of the other.
It can turn in many directions.
Types of movement: extension, flexion, abduction, adduction, rotation and
circumduction.
Examples are the shoulder and hip joints.
Pivot joint charecteristics
A peg on one bone fits into a ring on the other.
Type of movement: rotation.
An example is the neck joint between the atlas and the axis.
Hinge joint charecteristics
Gliding joint charecteristics
The flat ends of the bones glide over each other.
They allow limited movement in all directions.
Examples are the joints between the carpals and the joints between the tarsals.
Slightly movable joints charecteristics
They allow a small amount of movement between the bones.
They are also known as cartilaginous joints because they are joined by
ligaments and/or cartilage (which absorbs the movement).
Examples include the strong ligaments that hold the sternum and ribs
together, and the pads of cartilage that hold the vertebrae together and act as shock absorbers.
Type of bones
Long Bones, Short bones, Flat bones and Irregular Bones.
Name of bones, Short Bone: Carpal, Long Bone: Humerus, Flat Bone: Sterum and Irregular Bone: Vertebra
Flat Bone charecteristics and functions
They are normally flat and have a large surface area.
Their large surface provides areas for muscles to attach to.
They are responsible for protecting the organs.
Examples include the cranium, scapula and sternum.
Irregular Bones charecteristics and functions
They provide protection and support.
They are specially shaped to perform certain functions.
Examples include the vertebrae in the back for protecting the spinal cord.
Short Bone Charecteristics and Functions
They tend to be as long as they are wide.
They are small, light and very strong.
They are responsible for bearing weight, absorbing shock and making fine
movements.
Examples include the carpals and tarsals.