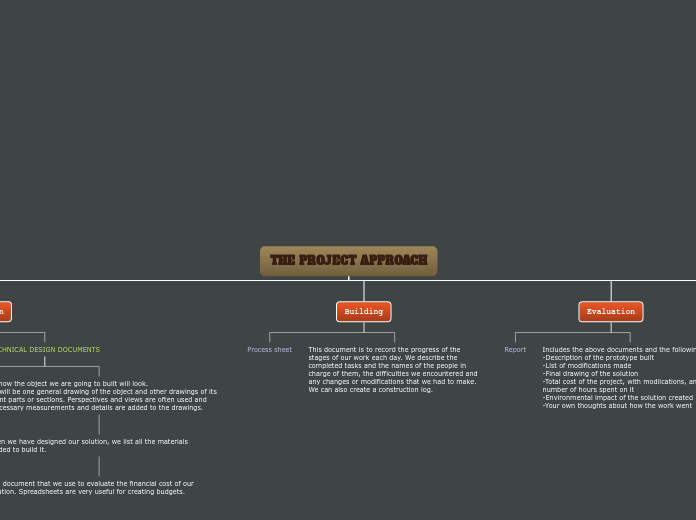
THE PROJECT APPROACH
Analyse
Detect the problem or need
Information and research
Search for possible solutions
Choose the solution
TYPE OF ANALISTS
Morphological
Functional
Technical
Economic
Social
Aesthetic
Historical
Shape of the object, its size, colour and basic
physical characteristics. Also sometimes its ergonomic characteristics.
-Utility: how it is used and the potential risks of its use.
- Also analyse the function of each part of the object.
Evaluation: how the object was made; the study of its materials, technology used to make it, how its parts are joined together and the environmental risks of the materials used.
The financial cost of manufacturing the product and its selling price. We study that the materials and manuacturing procedures used are cheap or make the product more expensive. We determine that the selling price of the object is correct by comparing it to similar objects.
-Study the object from the point of view of its social impact and analyse the human needs that it meets
-Evaluate its environmental impact and recyclability.
Evaluate how our senses react to the object, its appearence, whether we find it attractive, etc.
-Evaluate the possible reasons why the object emerged and its historical development.
-Analyse its possible future development.
Design
Design
Prepare and plan the work
TECHNICAL DESIGN DOCUMENTS
Drawings
List of materials and tools
Budget
Show how the object we are going to built will look.
There will be one general drawing of the object and other drawings of its different parts or sections. Perspectives and views are often used and the necessary measurements and details are added to the drawings.
When we have designed our solution, we list all the materials needed to build it.
The document that we use to evaluate the financial cost of our solution. Spreadsheets are very useful for creating budgets.
Building
Process sheet
This document is to record the progress of the stages of our work each day. We describe the completed tasks and the names of the people in charge of them, the difficulties we encountered and any changes or modifications that we had to make. We can also create a construction log.
Evaluation
Report
Includes the above documents and the followings:
-Description of the prototype built
-List of modifications made
-Final drawing of the solution
-Total cost of the project, with modiications, and the number of hours spent on it
-Environmental impact of the solution created
-Your own thoughts about how the work went
TECHNOLOGICAL PRODUCTS
Sales cycle
Price
Promotion
Distribution
Crucial element in the sale of a product.
It is part of bussiness strategy of companies.
Types: advertising campaigns on television, in news papers and on digital media. These campaigns target potential consumers and show them the products in an attractive way so that they will want to buy them.
Staple product like milk or bread do not need any promotion.
Most common distribution channels are wholesale, retail sale, online sale and franchises.
Sustainable technology
Innovation
Obsolence
Modification made to a product to adapt it to new
conditions brought about by changes in requirements or progress.
It means that some products have fallen into disuse because they do not have the functionality of the new technologies appearing on the market due to a lack of spare parts for their repair.
Positive influence:
-They have contributed to the development in society in many ways: we can now be independent of weather conditions; we are able to settle in one place; all members of society can communicate with each other, and our life expectancy has increased considerably.
Negative influence:
It has increased the use of fossil fuels; which has caused the deterioration of our environment, traffic jams because of the overuse of vehicles, health problems related to our environment , etc.
Product obsolence generates a build-up of waste. This waste is not generally biodegradable and it is highlky polluting.