The Relationship Between Parliament and the Courts in Law-Making
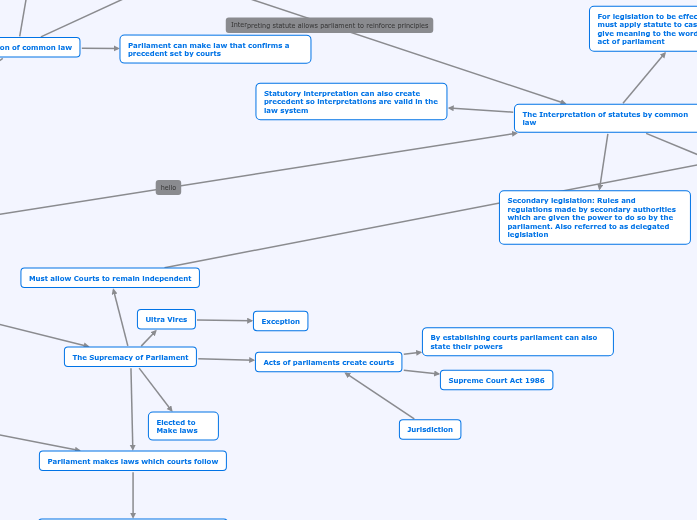
The Interpretation of statutes by common law
For legislation to be effective, the courts must apply statute to cases and interpret or give meaning to the word or phrase in an act of parliament
Secondary legislation: Rules and regulations made by secondary authorities which are given the power to do so by the parliament. Also referred to as delegated legislation
'Deing v Tarola' was the studded belt case where a man was arrested for wearing a studded belt as it was classified as a ‘weapon’. The decision then made the precedent ‘An item that is not in common use as a weapon cannot be classified as a weapon' under the Control of Weapons Act
Without the courts, Parliament would need to pass new legislation more frequently. This is because most statute that is passed is drafted broadly allowing the courts to interpret them.
Statutory interpretation can also create precedent so interpretations are valid in the law system
Parliament Abrogates Common Law
Parliament has the power to pass legislation which abrogates the decision made through the courts with the exception of high court decisions made on constitutional matters
DPP v Closter 2014
Codification of common law
For Example in the Mabo case the parliament passed the native title act after the High Court ruled in favour of Mabo.
Parliament can make law that confirms a precedent set by courts
Involves parliament passing legislation that reinforces principles established in the courts ruling
The Supremacy of Parliament
Elected to Make laws
Parliament makes laws which courts follow
Can set out maximum sentences and mandatory minimum sentences for courts to follow
Magistrates court act 1989
Lists
Koori Court
Offences
Acts of parliaments create courts
Supreme Court Act 1986
By establishing courts parliament can also state their powers
Ultra Vires
Exception
Must allow Courts to remain independent
The Ability of Courts to Influence Parliament
Courts make comments in their judgement
Parliament responds to decisions made by courts
Subtopic
Disapproval
E.g. Trigwell case