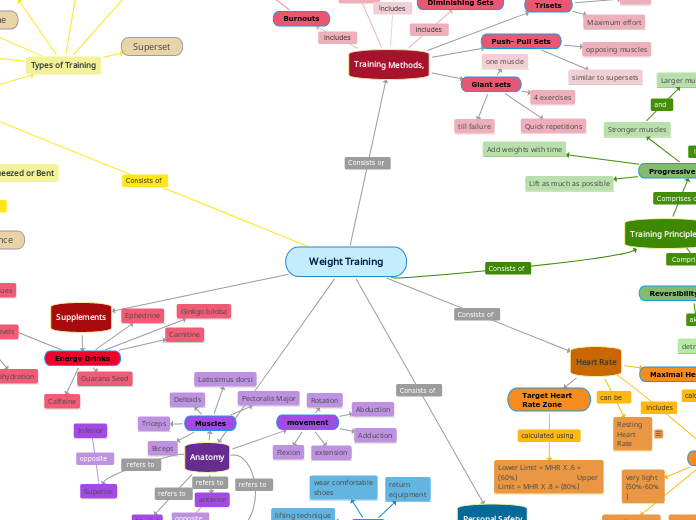
Weight Training
Resistance Training
Strength Training
Pushed, Pulled, Squeezed or Bent
Resistance
Load
Equipment or Bodyweight
Types of Training
Multi-set
Pyramid
Superset
Dropsets
Circuit Training
Split Training Routine
Contracting Muscles
power, hypertrophy, and/or endurance.
Benefits
Strength
in
bone
muscle
tendon
ligaments
bone density
improved joint function
reduced injury
increased metabolism
Training Principles
Progressive Overload
Lift as much as possible
Add weights with time
Stronger muscles
Larger muscles
Gain
endurance
Strength
FITT
Reversibility Principle
lose gains
detraining
Specificity Principle
Focuses on
specific muscle
specific fitness
Specific to an individual
used to build
agility
speed
endurance
power
Training Methods,
Split Training
2 muscle groups per day
Circuit Training
many exercises, less intervals
Cardiovascular
Similar to aerobic
Burnouts
+ weights -reps
Diminishing Sets
20 reps/ per set
70 reps in little sets
Trisets
2+ exercises of similar motion
no rest
Maximum effort
Push- Pull Sets
opposing muscles
similar to supersets
Giant sets
one muscle
4 exercises
Quick repetitions
till failure
Heart Rate
Resting Heart Rate
Maximal Heart Rate
MHR = 220 – age (W)MHR 226-age
Target Heart Rate Zone
Lower Limit = MHR X .6 = (60%) Upper Limit = MHR X .8 = (80%)
Zones
very light (50%-60%)
light (60%-70%
moderate (70%-80%)
hard (80%-90%)
maximum (90%-100%)
Personal Safety
Do's
use spotters
back straight
lifting technique
wear comfortable shoes
return equipment
control breathing
Don't
stop when lightheaded
over work
skip warmup
ignore pain
stand on uneven ground
skip cool down
Anatomy
anterior
posterior
Superior
Inferior
Medial
lateral
proximal
distal
movement
Flexion
extension
Adduction
Abduction
Rotation
Muscles
Pectoralis Major
Deltoids
Biceps
Triceps
Latissimus dorsi
Supplements
Energy Drinks
Guarana Seed
Carnitine
Ephedrine
Ginkgo biloba
Caffeine
Side Effects
High caloric levels
Very expensive
Dehydration
Nausea
vomiting
shakiness
liver issues