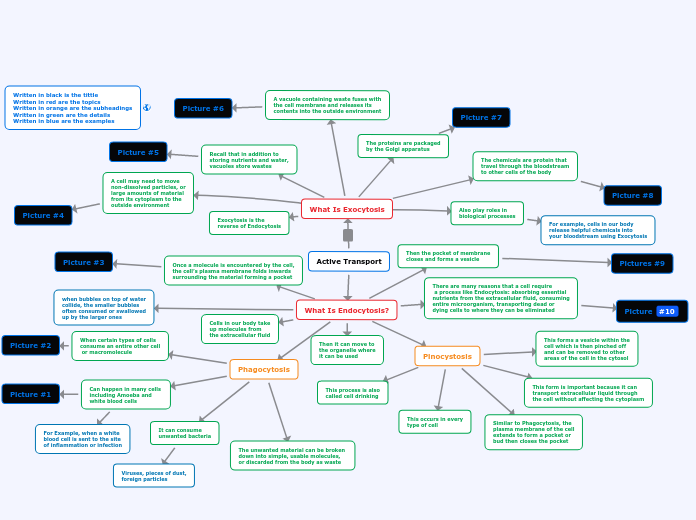
Written in black is the tittle
Written in red are the topics
Written in orange are the subheadings
Written in green are the details
Written in blue are the examples
Active Transport
What Is Exocytosis
The chemicals are protein that
travel through the bloodstream
to other cells of the body
Picture #8
The proteins are packaged
by the Golgi apparatus
Picture #7
A vacuole containing waste fuses with
the cell membrane and releases its
contents into the outside environment
Picture #6
Also play roles in
biological processes
For example, cells in our body
release helpful chemicals into
your bloodstream using Exocytosis
Recall that in addition to
storing nutrients and water,
vacuoles store wastes
Picture #5
A cell may need to move
non-dissolved particles, or
large amounts of material
from its cytoplasm to the
outside environment
Picture #4
Exocytosis is the
reverse of Endocytosis
What Is Endocytosis?
Then it can move to
the organelle where
it can be used
Then the pocket of membrane
closes and forms a vesicle
Pictures #9
Once a molecule is encountered by the cell,
the cell’s plasma membrane folds inwards
surrounding the material forming a pocket
Picture #3
There are many reasons that a cell require
a process like Endocytosis: absorbing essential
nutrients from the extracellular fluid, consuming
entire microorganism, transporting dead or
dying cells to where they can be eliminated
Picture #10
Cells in our body take
up molecules from
the extracellular fluid
when bubbles on top of water
collide, the smaller bubbles
often consumed or swallowed
up by the larger ones
Pinocystosis
This form is important because it can
transport extracellular liquid through
the cell without affecting the cytoplasm
Similar to Phagocytosis, the
plasma membrane of the cell
extends to form a pocket or
bud then closes the pocket
This forms a vesicle within the
cell which is then pinched off
and can be removed to other
areas of the cell in the cytosol
This occurs in every
type of cell
This process is also
called cell drinking
Phagocytosis
The unwanted material can be broken
down into simple, usable molecules,
or discarded from the body as waste
It can consume
unwanted bacteria
Viruses, pieces of dust,
foreign particles
Can happen in many cells
including Amoeba and
white blood cells
Picture #1
For Example, when a white
blood cell is sent to the site
of inflammation or infection
When certain types of cells
consume an entire other cell
or macromolecule
Picture #2