par Josef Pentick-Weichert Il y a 2 années
224
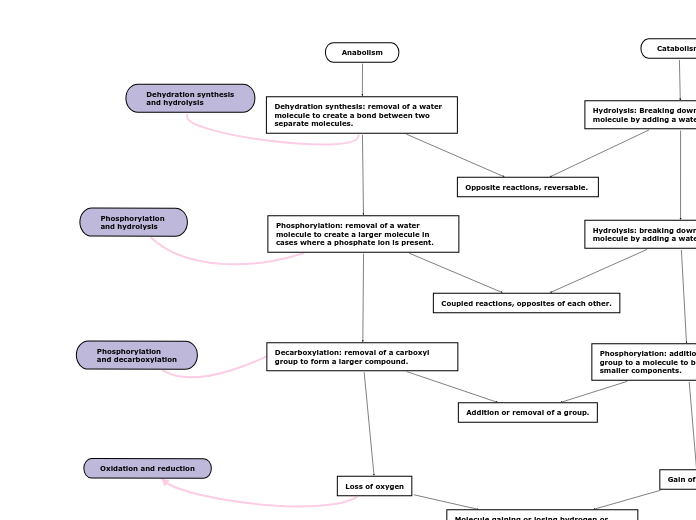
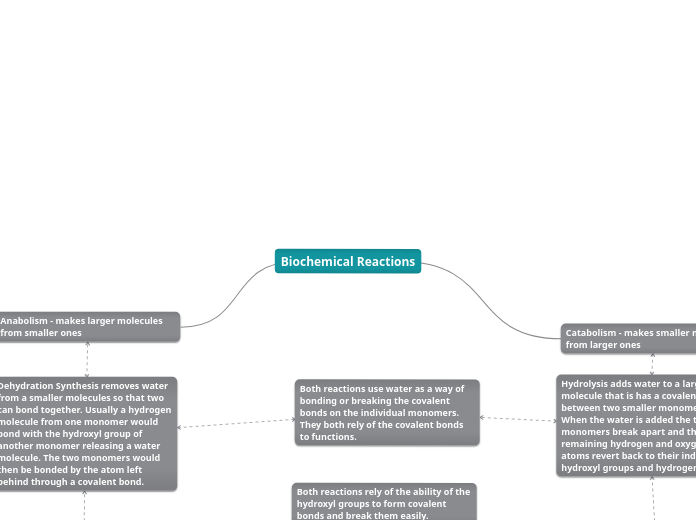
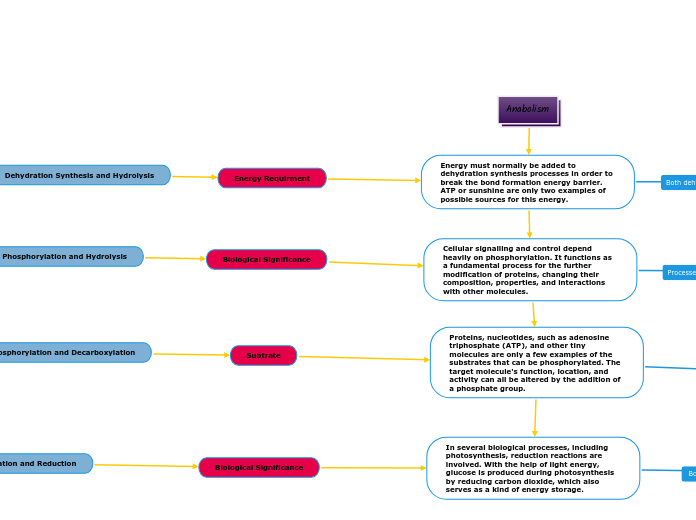
Anabolism
The text discusses several biochemical processes that are fundamental to cellular metabolism. Anabolism involves the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler ones, often through dehydration synthesis, which removes a water molecule to form new bonds.