IMOSSIO Magloire
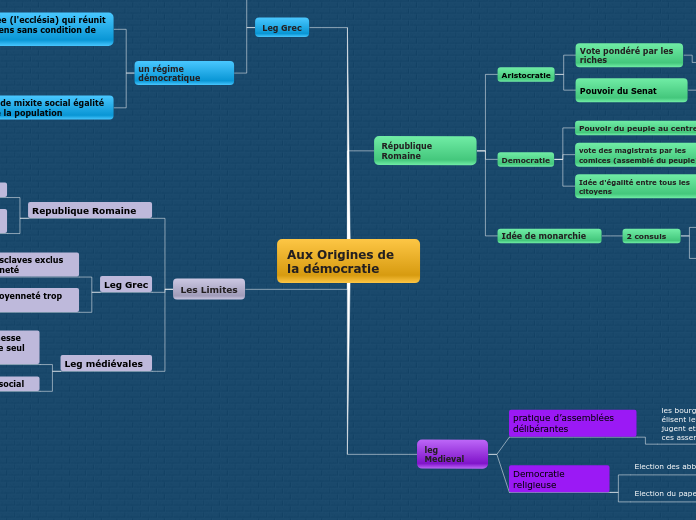
Aux Origines de la démocratie
Seek to understand how this civilization had evolved into becoming one of the most powerful in history.
Learn about Greek scientific breakthroughs, great battles, and mysterious stories with gods and goddesses.
Les Limites
Leg médiévales
Ares, son of Zeus and Hera, was the god of war.
He was disliked both by his parents and by the people. Though the god of war, he was considered to be a coward.
Dicrimination social
les plus pauvre subisse ce que les plus riches veulent (vote)
Toutes les richesse détenu par une seul personne
Also, called the 'cloud-gatherer' and 'thunderer' by the Greek poet Hesiod, Zeus was the supreme ruler of the Olympian gods. He controlled the weather, and every time lightning struck, people thought it was a sign from Zeus.
Un taux de citoyenneté trop faible
30 mille citoyen pour environ 305 000 individus
Femmes et esclaves exclus de la citoyenneté
How was he symbolized?
Type in the answers. Example: sometimes seated on a throne.
Republique Romaine
Poseidon, brother of Zeus, was the god of the sea and protector of all waters.
He was also the god of horses. There is a myth about Poseidon creating the first horse in order to impress his beloved Demeter.
inégalité sur les droits politiques
les citoyens ne jouissent pas des mêmes droits politiques (droit de vote), civils (accès à la propriété) et religieux (accès au sacerdoce)
Where are his temples and sacred places?
Type in the answers.
Régime oligarchique
Symbol
How was he symbolized?
Type in the answers.
Leg Grec
Greek Mythology was part of the religion in Ancient Greece and it included all the myths and teachings of their gods, the origins of the world and the Greek cult and ritual practices.
un régime démocratique
Hera was the wife of Zeus.
She was the patron of weddings and marriage. Her jealousy is well-known throughout history because she used to take awful revenge on Zeus' lovers and illegitimate children.
Idée de mixite social égalité entre la population
les enfants des plus riches reçoivent la même éducation que ceux des plus pauvres
Tirage au sort
le but est de faire participer davantage les plus pauvres à la vie de la cité.
Where are her temples and sacred places?
Type in geographical locations.
Une assemblée (l'ecclésia) qui réunit tous les citoyens sans condition de richesse.
les citoyens exercent directement les responsabilités de la cité.
L'Ecclésia délègue une partie de ses pouvoirs aux magistrats
How was she symbolized?
Type in the answers. Example: a high crown.
Démocratie participative
Apollo son of Zeus and Letto was the god of the sun, truth, music, poetry, dance, and healing.
Vote par de tout les citoyens
Where are his temples and sacred places?
Type in geographical locations.
tout les citoyens ont droit au débat
Assemble des citoyen au Pnyx
How was he symbolized?
He had 2 symbols, one in time of peace, one in time of war. Type in the answers.
leg Medieval
Democratie religieuse
Election du pape
Election des abbés
Discoveries of Pythagoras of Samos (570 - 495 B.C.)
Pythagoras of Samos was a Greek philosopher, mathematician, astronomer, and the founder of the religious movement called 'Pythagoreanism'. Type in his most important discoveries.
pratique d’assemblées délibérantes
les bourgeois du Moyen Âge élisent leurs magistrats, jugent et punissent lors des ces assemblés
Discoveries of Thales of Miletus (620 - 546 B.C.)
Thales of Miletus was one of the Seven Wise Men of Greece, a prolific philosopher, geometer, military engineer, and astronomer. Type in the most important discoveries made by him.
République Romaine
Most important battles in Ancient Greece
Already internally warring, Ancient Greece has fought many battles with external enemies, but four of them were extremely significant: Battle of Marathon (490 B.C.), Battle of Salamis (480 B.C.), Battle of Thermopylae (480 B.C.), and Battle of Chaeronea (338 B.C.).
Idée de monarchie
2 consuls
Dirigeant de l'armé
Think of any interesting facts related to this battle, or figures related to soldiers, casualties, etc. Type them in.
Dirigeant de l'état
Who was the enemy against which the Greeks fought at Thermopylae?
Type in the answer.
Democratie
Idée d'égalité entre tous les citoyens
vote des magistrats par les comices (assemblé du peuple)
Pouvoir du peuple au centre
Which army won the battle?
Type in the answer.
vote les lois et les guerres
Aristocratie
Pouvoir du Senat
Approuve les lois, dirige les finances et les activité étrangère
Leader of the Greek army
Who led the Greek army in the Battle of Marathon?
Type in the answer.
Vote pondéré par les riches
un grand pouvoir confié aux riches
Who was the enemy against which the Greeks fought at Marathon?
Type in the answer.