Basic aspect about methodology of the english teaching
Procedure
fact that it is the actual development of the teaching in the classroom.
elements: (syllabus, learners, students, and materials)
help students learn effectively
teaching learning proces
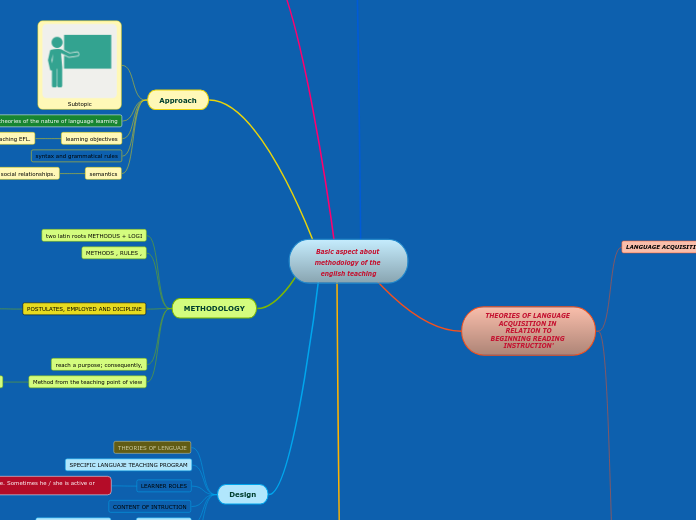
Design
INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIALS
TEACHER ROLES
self-prepared materials.
CONTENT OF INTRUCTION
LEARNER ROLES
in the teaching procedure. Sometimes he / she is active or passive.
SPECIFIC LANGUAJE TEACHING PROGRAM
THEORIES OF LENGUAJE
METHODOLOGY
Method from the teaching point of view
can be divided into approach, design, and procedure;
reach a purpose; consequently,
POSTULATES, EMPLOYED AND DICIPLINE
METHODS , RULES ,
two latin roots METHODUS + LOGI
Approach
semantics
the facilitation of personal and social relationships.
syntax and grammatical rules
learning objectives
teaching approaches and methods for teaching EFL.
he theories of the nature of language learning
Basic aspects
Teaching
teachers to help students to study or review new facts.
Learning
Learning is a conscious process for understanding new facts.
Language
sounds, letters, words, phrases, sentences, and finally speech
THEORIES OF LANGUAGE ACQUISITION IN RELATION TO
BEGINNING READING INSTRUCTION'
LANGUAGE LEARNING
Standard English
theory of language or a general theory of learning.
developments in modern linguistics
study of language acquisition.
LANGUAGE ACQUISITION
Cognitive The or ie s
critical determinant of language acquisition.
the ability to segment utterances into sounds and
meanings
linguistic data
recognized.
linguistic principles;
the mental ability to retain
items in short term memory,
the observed linguistic and changes
express new
meanings,
habilities of the child develop.
Behavioristic Theories
the abstract nature of linguistic
knowledge.
Language is a mentalistic phenomenon,
acquired through operant
conditioning
concepts are irrelevant in explaining linguistic behavior
process of acquiring language.
contextual generalization.
the child must learn
abstract structures
Nativist Theories
cognitive developments allow it to emerge.
Learning, as this term is traditionally defined, is not involved.
studies of normal
language development in children
abnormal language development
Language emerges during this
maturational
Subtopic
The learning mechanisms
modes of perception, abilities in categorization, and capacities
(reflections in language of specific linguistic abilities
A8. CRISTIAN IZA.LEARNING CONTEX.