par Ramon Alvarez Il y a 12 années
310
Biology 311D Concept Map - RAA2446
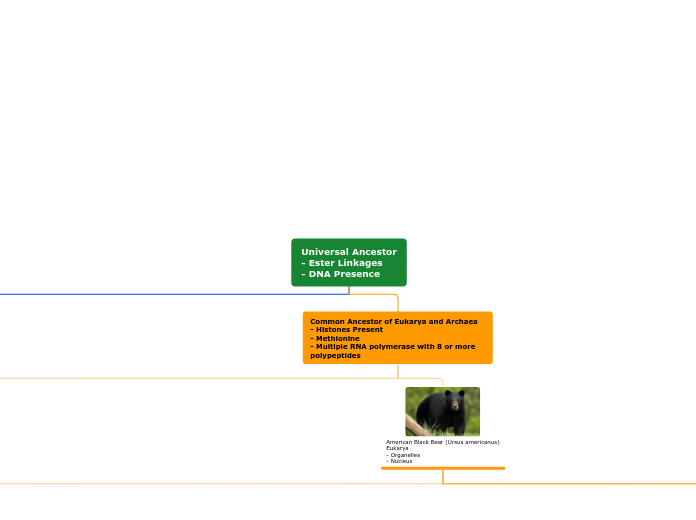
The concept map delves into various aspects of evolutionary biology, highlighting the mechanisms and factors influencing changes in gene frequency over generations. It discusses natural selection and its three modes—