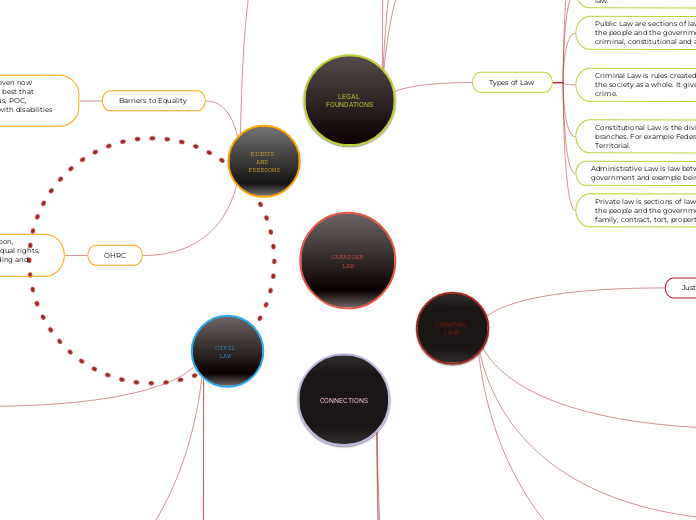
CONNECTIONS
Legal foundations as a whole connects to everything. Because without such foundations there is nothing to build upon. The rights provided have allowed for a free society to flourish now that is constantly changing to fit todays standards.
Legal foundations and Rights and Freedoms
Legal foundations are the basis of the Canadian legal system it provided the rule of law and laws that have been built upon and altered throughout the decades of our country. It brings upon the constitution with which includes the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms that protects the rights and freedoms of all Canadians regardless of race, religion, sex ect ect...
Civil and Criminal Law
Criminal law and civil law connect as they are both sections of law that can overlap. They work similarly but they focus one two separate type of cases with different types of punishment. Civil focuses on civil cases/situations regarding family, injury, divorce, custody, contarcts trespassing and mainly property. Criminal law focuses on serious crime against people.
RIGHTS AND FREEDOMS
OHRC
Human rights that cannot be infringed upon, individual dignity and worth, entitled to equal rights, no discrimination and mutual understanding and respect.
Remedial way of solving workplace issues
Barriers to Equality
There are many barriers to equality even now although it has improved its not the best that equality can be. Women's, indigenous, POC, immigrants, 2SLGBTQ+ and people with disabilities still face discrimination
Example being the Lesiuk v. Canada case, this case was about a law that would only benefited white cis men without taking to account women of all colors, indigenous peoples, recent immigrants, disabled people, and just anyone that was not a white man rights. The law Concerned eligibility for employment benefits, specifically for women. Employment Insurance Act required women to have worked 700 hours to qualify for benefits. LEAF argued that the eligibility requirements discriminated against women and violated s. 15. The eligibility only took men into account. The restriction for qualifying based on hours unfairly barred women from receiving benefits. It valued full-time, year-round, paid work performed by men. The requirements were not made for paid and unpaid work performed by women. Men and women have different working patterns. The working pattern of men was only taken into account.
Charter of Rights and Freedoms
The Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms protects and outlines all persons in Canada rights and freedoms. It outlines the rights and freedoms we have as citizens and newcomers to Canada.
It forms part of the Constitution.
A human right is a right that is given by a default that applies regardless of gender, race, religion, dead or alive ect…
Natural rights are universal rights that are not set up in law or customs and they are fundamental rights that cannot be repelled such as the right to freedoms of speech, privacy, and more.
Rights have evolved throughout the centuries and have come to the final of, Mankind is equal, governments are only powerful because of mankind and that governments that go against the will of the people, represses the people and harms the people will be altered or abolished by mankind.
Political freedom, freedom of speech, rule of law and equality.
CIVIL LAW
Employment Law
Anyone harmed in work is entitled to workers compensation
Workers compensation is the right be compensated after suffering an injury or illness related to a workers employment. An example that would give you the right for compensation is if you fell and hurt your break on the job or you got into a crash while delivering ect ect...
Union is a group of workers working together to achieve a mutual goal in the same job. The role of a union is to increase worker abilities of getting better work contracts and improved workplace environments. A union would be a collective contract between all employees involved and their employer. An example of how a union is operated is listed under the Canada Labor Code.
Collective bargaining is the way a unions contract gets created by the employer and the employees mutually agreeing to a set of conditions.
Human rights legislation protects worker rights
Ensures min wage, min age, work hours, leaves, fires and holidays.
Contract Law
Building blocks of a contract includes intention to contract, offer and acceptances, consideration and certainty of the terms.
For example in the show suits Keith who had a history of being an alcoholic and gambler participates in a risky poker match with a contract he did not accept sober. Tommy the man who abused the fact Keith was drunk created a legally binding contract on a napkin with Keith where he would lend him 3 million and 5 hundred dollars and that if Keith did not win at the end of the play with his current hand of poker then his company would be given as collateral.
Written legally binding contract (the napkin)
Intention to contract, both Keith and Tommy intended to create a legally binding relationship in regards to the 3 million dollars and company
- Offer and acceptance are displayed because the offer on the napkin outlines terms and with the intention of creating a legally binding contract once the person it is being given to consents
- Consideration was addressed in the contract by having Keith promise his company as collateral and Tommy promising the 3 million dollars and 5 hundred as a loan
There are 3 types of contracts, unilateral, bilateral and implied contract.
Implied contract is a contract never explicitly stated however it is assumed that both parties are aware of it. An example is agreeing not to steal and enter a store with the intent of purchasing.
Bilateral contract is where two parties agree on terms what will be exchanged for what and then consent to it and make it legally binding.
Unilateral contract is the opposite of an bilateral in the way that only one party promises something in exchange for an action. An example is a reward being promised for finding a missing pet from a missing poster.
Family Law
Family Law has many different parts such important parts include divorce, common law, annulment, separation, crown wardship and custody.
Crown wardship is when the court finds that neither parents can take care of their child thus needing to put them into foster care. It is an order where the court is legally allowed to take a child away from both parents. An example can be where both parents are unfit to take care of the child's needs by fact od being abusive, drug addicted, alcoholic ect ect...
Access is given to a parent who is in joint custody of a child. Types of access consist of supervised, specified or reasonable.
Separation is a form of divorce without being divorced. Signing a separations paper will allow for both partners to figure out issues such as house, car ect ect...
Custody is when partners who are no longer together have children one or both will have either custody or joint custody of a child in which a parent will stay as the guardian of a child.
Annulment is when a court order states that a marriage is no longer valid and is thus erased from existence.
Divorce is a legal procedure in which someone in a marriage wants to end it. It begins with a petition for divorce which is usually because on of the partners in the marriage is contesting against it.
Common law are relationships where two people who live together and engage romantically with one another for more than a year but have not married.
Tort Law
Example of tort case is the The Rankin v. JJ. Plaintiff J.J is suing neglect for the brain injury he received from the crash and the damages received to the car that C crashed into the highway.
Tort law is civil remedies for crimes that cause damage to people or property.
Types of torts
Intentional Torts is an act done on purpose that causes injury/damages.
Strict Liability is when there was injury and responsibility can be imposed on the wrong doer without need proof of carelessness.
Negligence is when a person with responsibility of care fails to provide it due to carelessness.
CRIMINAL LAW
Justice is blind however the people that deliver it are not
The justice system is systematically racist
Different approaches to justice can be more healthy and inclusive
Reintegration is the support given to offenders when they get let back into society after their prison sentence
Restorative justice is when the offender will be rehabilitated through being made to interact with the victim, victims family and community. It is a different way of justice that aims to allow the offender to understand the harm they have caused and change for the better.
There is a higher proportion of POC in prison, especially Indigenous/black people (usually wrongly accused)
Often times they will lack support/family/friends after a crime making it more likely to re-offend because they have nothing else.
Change
During 1984-1991 crime by youth had peaked because of the "Zero Policy Act"
Zero tolerance is a quote used to define a policy that provides a severe punishment for a specific offense. During 1984- 1991 youth were criminalized like adults and often mistreated.
Youth commit crimes because of peer pressure, impulsivity and troubles in family/home/school life.
During 1908 a different approach was taken to deal with kids who had committed crimes. It was the Juvenile Delinquents Act where youth would be treated as misguided kids instead of criminals by sending them to training schools however it was considered too soft because of the many re-offenders.
During 2002 Youth Criminal Justice Act had the purpose of giving long-term protection to society by making sentences match the crime. Family of the youths family, victims, youth workers and more would get involved similar to restorative justice. This was done to combat the fact Canada had the highest rate of youth in prison during 2002.
Police
In order to arrest the police must always identify themselves, tell the accused they are arrested, tell the accused they have the right to a lawyer and tell them their charges.
Police have the rights to search accused, take accused to police station, take away possessions of accused and with a warrant get DNA. They also have the right to use extra force against someone restraining against arrest or is being a danger to others/themselves.
When police search for evidence anywhere they require a searching warrant. A warrant in criminal law is basically the right to search an area with reasonable grounds to believe that either a criminal act was commited, evidence that incriminates and bears an offense or anything that was intended to be used in the purpose of harm.
Justice is blind
Canada's criminal law of justice aims to protect the people and pave the way to justice using fairness/honesty
Innocent till proven guilty
In order to be proven guilty there must be a burden of proof given to the crown to be able to believe "guilt beyond a reasonable doubt" If the crown has no proof then they cannot legally detain a person regardless
There are different types of crime
Assault, mischief, robbery, manslaughter, impaired driving, fraud, failure to appear, break & enter, parking infraction, trespassing at night, vandalism, failure to stop, theft, disturbing the peace and possession of controlled substances ect ect...
Offences
Summary offense is an offense that is solved without the need of a jury nor an indictment. Indictable offense is when a serious crime has been committed and can lead to prison. Hybrid offense means there is an option of the crown choosing summary or indictable.
Aims to achieve deterrence, rehabilitation, retribution and segregation
Actus reus the guilty act and mens rea the guilty mind
Example of this is during the mock trial our class had organized. The young girl who was accused of stealing an Ipod had committed a guilty act however she did not have a guilty mind. She was let out innocent from the court because she lacked mens rea.
Criminal law focuses on manslaughter, criminal offences against the people
LEGAL FOUNDATIONS
Types of Law
Private law is sections of law that interact between the people and the government. There is 5 types, family, contract, tort, property, and labor law.
Administrative Law is law between citizens and government and example being LCBO.
Constitutional Law is the dividing of power with branches. For example Federal, Provincial and Territorial.
Criminal Law is rules created against offences against the society as a whole. It gives consequences for crime.
How are the laws made?
Laws in Canada are introduced by way of bills. A bill is a proposal for a law to be potentially introduced. Bills are brought forth in the House of Commons by Senators which are then discussed and debated on its merits. If approved, it will be introduced as an official law.
Public Law are sections of law that interact between the people and the government. There are 3 types, criminal, constitutional and administrative law.
Substantive Law are sets of laws that give punishment for crimes and can be in public/private law.
Procedural Law is laws regarding the process in which the law works. for example is it being done ethically?
Ppolitical parties
Canadas government is made up of political parties who are reflective of its countries people. These parties beliefs range from a spectrum called the “Political Spectrum” that ranges from the left, center and right.
Liberal, Conservative, NDP, Green and Bloc Québécois are the main parties that participate in elections.
The Constitution
The Constitution is the supreme law of Canada and all laws must abide by it.
The Canadian Constitution outlines the rules for how Canada is governed. It outlines responsibilities of the 3 branches of government (Legislative,Executive,Judicial) It also outlines the duties of the federal and provincial government.
The Constitution includes the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms and also protects the rights of indigenous peoples.
Rule of law is a concept that we are ruled by laws but not people. It brings the idea that we are equal no matter our wealth, our appearances ect ect under law.
Precedent is something that happened before that can be used as a guide because it is a unique case that can be referenced an example of such is the case Roncarelli v. Duplessis where government used their power for personal gain against the people. The reason this case is so important is because it laid down the base for the pre- Charter of Rights.
CANADIAN LAW