par marwa jasim Il y a 1 année
103
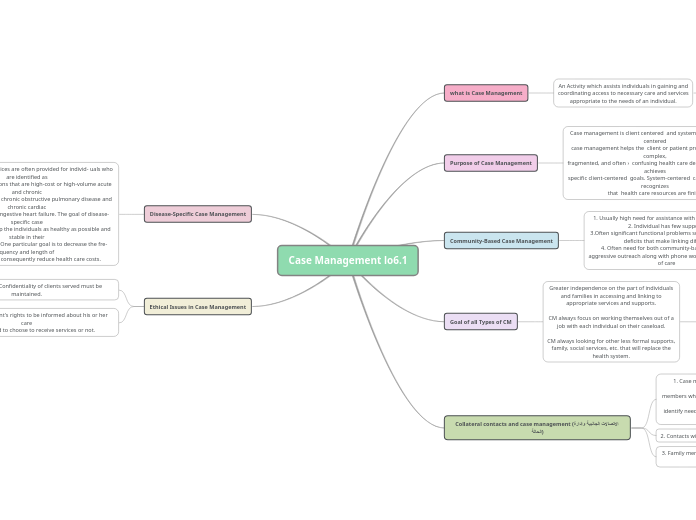
Case Management lo6.1
Case management serves dual purposes, focusing on both client-centered and system-centered approaches. Client-centered case management aims to help patients navigate a complex healthcare system to achieve personalized goals, while system-centered case management acknowledges the limitations of healthcare resources.