CH 2: The Research Enterprise in Psychology
Ethical Guidelines in Canada
The Canadian Psychological Association has principles regarding how people whom the psychologist comes into contact with should be treated. All people should be treated with dignity and psychologists should ensure that their value is not dependent upon culture, race, or nationality. Psychologists have a personal responsibility to protect the rights, privacy, and personal liberty of others. Psychologists are also expected to protect the vulnerable such as children.
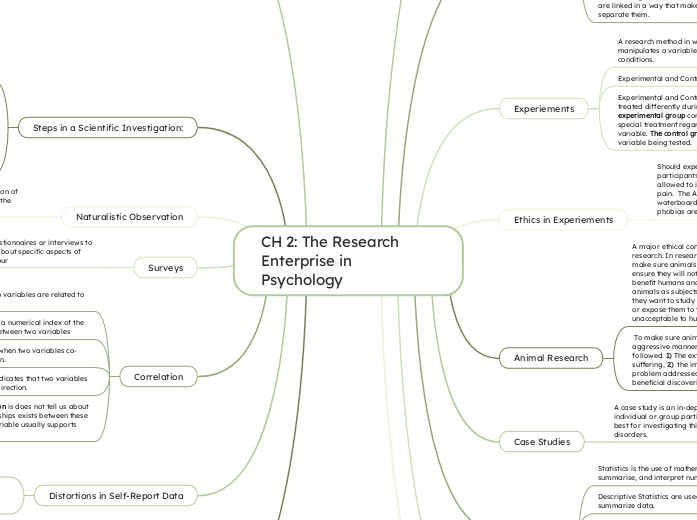
Distortions in Self-Report Data
A response set is a tendency to respond to questions in a particular way that is unrelated to the content of the questions.
Social desirability bias is a tendency to give socially approved answers about oneself.
Correlation
Correlation and Causation is does not tell us about the cause-effect relationships exists between these two variables. A third variable usually supports further investigation
A negative correlation indicates that two variables co-vary in the opposite direction.
A positive correlation is when two variables co-vary in the same direction.
Correlation coefficient is a numerical index of the degree of relationship between two variables
A correlation is when two variables are related to each other.
Surveys
Researchers use questionnaires or interviews to gather information about specific aspects of participant's behaviour
Naturalistic Observation
A researcher engages in careful observation of behavior without intervening directly with the subjects.
Steps in a Scientific Investigation:
Translating a theory or idea into a testable hypothesis. Scientific hypothesis must me formulated precisely and the variables must be clearly defined
Step 1: Formulate a testable hypothesis
Researching on how to put the hypothesis to an empirical test. The researcher must look at the pros and cons, then select the strategy that seems to be the most important and practical.
Step 2: Selecting Research Methods and Design the Study
Researchers use many resources to collect data, which are procedures for making empirical observations and measurements. Commonly used techniques are observations, questionnaires, interviews, psychological tests
Step 3: Collect the Data
Researchers use statistics to analyze their data and to decide whether their hypothesis have been supported
Step 4: Analyze the Data and Draw Conclusions
Scientific progress can only be achieved if researchers share their findings with one another and the general public. The final step is to write up a concise summary of the study and its findings
Step 5: Report the Findings:
Hypothesis
A hypothesis is a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables
Experimental Bias
This can be an error in research as it occurs when a researcher's expectations about the outcome of a study influence the results.
Samples
Sampling bias exists when a sample is not representative of the population from which it was drawn.
A sample is the subjects selected for observation in an empirical study. Though the population is much larger than what the researcher wants to study. Researchers usually like to generalize.
Statistics
Statistical significance exists when the probability that observed findings are due to chance is very low.
Inferential statistics are used to interpret data and draw conclusions.
Descriptive Statistics are used to orginize and summarize data.
Statistics is the use of mathematics to organize, summarise, and interpret numerical data
Case Studies
A case study is an in-depth investigation of an individual or group participant. Case studies are best for investigating things such as psychological disorders.
Animal Research
To make sure animals are not harmed in any aggressive manner, three guidelines should be followed. 1) The extent of anticipated animal suffering, 2) the importance of the research problem addressed, and 3) the likelihood of beneficial discoveries.
A major ethical controversy is the use of animals in research. In research, efforts must be made to make sure animals do not feel discomfort and to ensure they will not be used unless the results benefit humans and animals. psychologists use animals as subjects for many reasons. Sometimes they want to study the behavior of a certain animal or expose them to treatments that would be unacceptable to human participants.
Ethics in Experiements
Should experimenters be able to manipulate participants' emotions? Researchers are not allowed to induce their subjects to any torture or pain. The APA stated techniques such as waterboarding, sexual assault, and exploitation of phobias are NOT allowed
Experiements
Experimental and Control groups are usually treated differently during an experiment. The experimental group comprises subjects who get special treatment regarding the independent variable. The control group does not receive the variable being tested.
Experimental and Control Groups
A research method in which the investigator manipulates a variable under carefully controlled conditions.
Variables
Confounding variable occurs when two variables are linked in a way that makes it difficult to separate them.
Extraneous variables are variables other than the IV that might influence the DV.
Dependent Variable is the variable that changes due to the manipulation caused by the independent variable.
Independent Variable is a condition or event that an experimenter manipulates to see its impact on the dependent variable.
Variables are measurable conditions, events, characters, or behaviors that are controlled by the study.
Goals of the Scientific Enterprise
Developing mesurement techniques that make it possible to describe behaviour clearly and precisly
Step 1: Measurement and Description
Scientists believe that they can properly explain the reason for occurrence of events. This is why hypothesis are created.
Step 2: Understanding and Prediction
Once people properly understand a phenomenon, they can take more control out of it
Step 3: Application and Control