par Justin Proffitt [STUDENT] Il y a 5 années
564
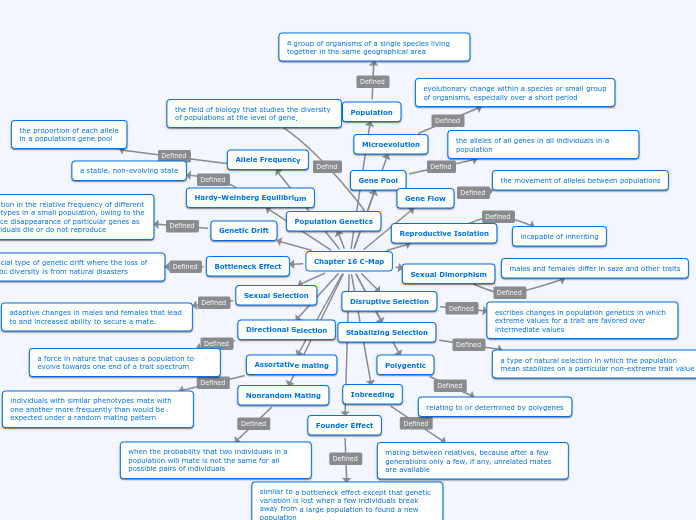
Chapter 16 C-Map
The chapter delves into various mechanisms and concepts in population genetics and evolutionary biology. It explores directional selection, a natural force driving populations towards one end of a trait spectrum, and sexual selection, which involves changes in males and females to enhance mate acquisition.