par samantha martin Il y a 3 années
205
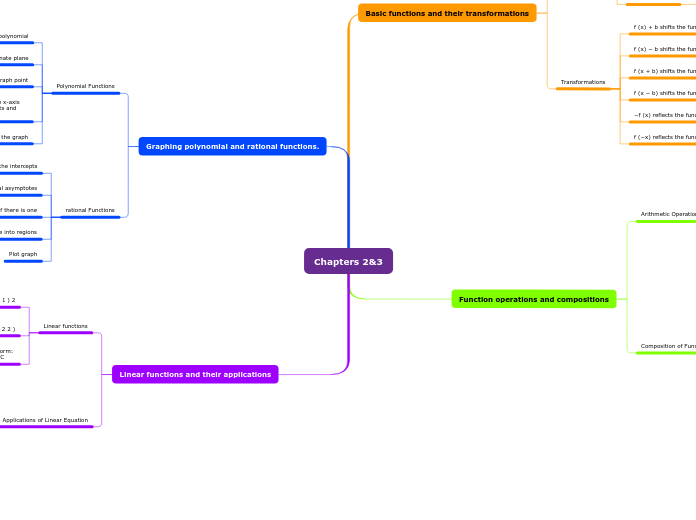
Chapters 2&3
The concepts covered include various fundamental functions and their transformations. Essential functions such as absolute value, squaring, cubing, and root functions are outlined, along with their mathematical expressions.