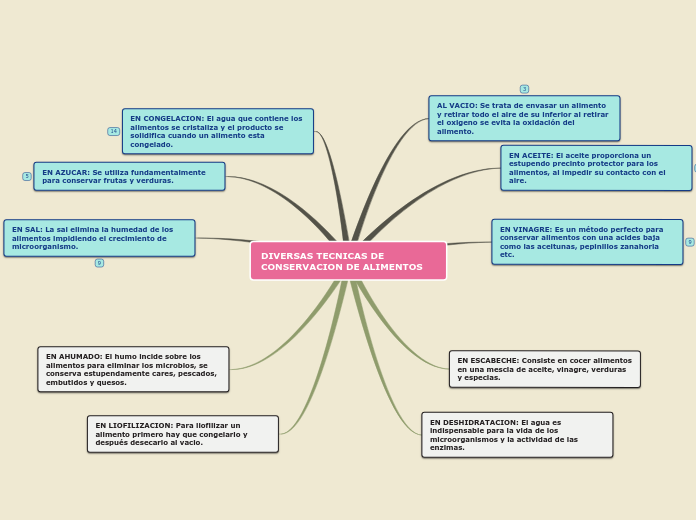
Barriers to Development
Oil Dependence
Limits financial development
Price volatility
Ethnic/Religious Conflict
Tribal groups
Shia and Sunni Islam
Geography
Strategic location
Lack of natural resources
State Capacity/ Institutions
Political
Legitimate third parties
Ineffective government/
Democratic institutions
Economic
Wealth contained by oligarchical elites
Lack of economic diversification
Southern Separatists: UAE
Houthi Forces: Iran
Government forces: Saudi Arabia and US
2014: New constitution to include for Houthis and South; Houthis take Sanaa
2015-Present: ISIS and Civil War
2020
COVID-19 prompts ceasefire
2019
Military withdraw by UAE
2018
Southern separatists backed by UAE take Aden
2015
Saudi led coalition launches airstrikes against Houthis in Arden
President Hadi flees south
ISIS kills 137 people
2005- 2014: Houthi Insurgency and Calls for Reform
Government Reform
2005: 36 dead in clashes between protestors and police
2007: Clashes between army and tribesman leave 16 dead
2008: Demands for electoral reform; accusations of northern bias
2011: President Selah steps down; President Hadi assumes control
Houthi Insurgency
2005: 200 killed in fighting
2007: After more death, Abdul-Malilk al-Houthi
accepts ceasefire
2008: Renewed fighting
2009: Clashes between rebels and Saudi forces
1994-2004: Terrorism and Civil Strife
Civil Conflict
2001: Violence during elections
calls for constitutional reform
2004: Hussein al-Houthi is martyred
Terrorism
2000: USS Cole
2002: Limburg
1994: War of Sucession
South attempts to succeed; defeated by national army
1990-1994: Transition
Democracy served as a barrier: Poor dispute resolution
Continued mistrust
No plan for how institutions would look in a unified state
Military never integrated
1990: Unification
Four major groups
Al-Hiraak
Houthis
Northern non-Islamists
Sunni Islamists
Reasons for unifying
Soviet Union collapses
oil and natural gas
decrease border tensions
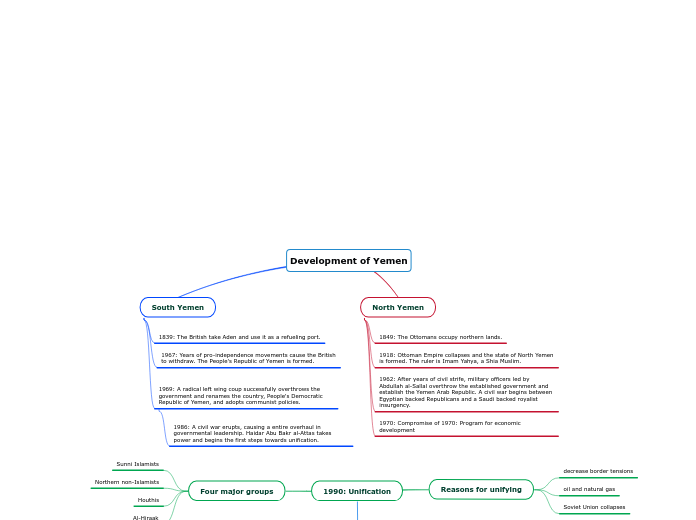
Development of Yemen
North Yemen
1970: Compromise of 1970: Program for economic development
1962: After years of civil strife, military officers led by Abdullah al-Sallal overthrow the established government and establish the Yemen Arab Republic. A civil war begins between Egyptian backed Republicans and a Saudi backed royalist insurgency.
1918: Ottoman Empire collapses and the state of North Yemen is formed. The ruler is Imam Yahya, a Shia Muslim.
1849: The Ottomans occupy northern lands.
South Yemen
1969: A radical left wing coup successfully overthrows the government and renames the country, People's Democratic Republic of Yemen, and adopts communist policies.
1986: A civil war erupts, causing a entire overhaul in governmental leadership. Haidar Abu Bakr al-Attas takes power and begins the first steps towards unification.
1967: Years of pro-independence movements cause the British to withdraw. The People's Republic of Yemen is formed.
1839: The British take Aden and use it as a refueling port.