par Jacqui Proud Il y a 6 années
352
ece111
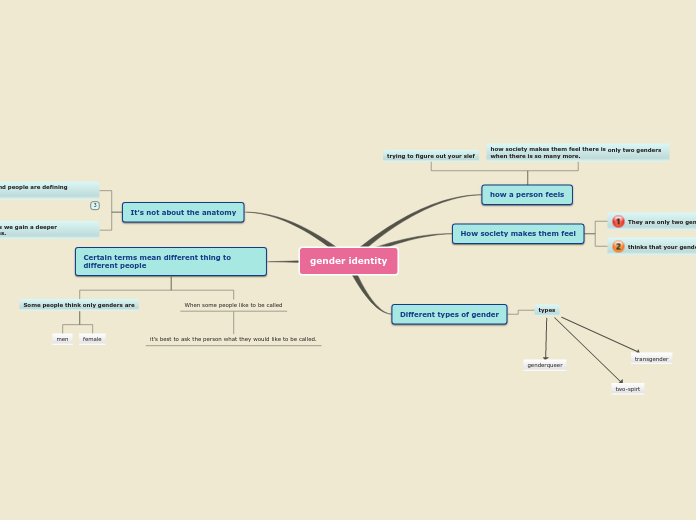
Children thrive when they are encouraged to be effective communicators, confident learners, and have a strong sense of identity. They use various forms of communication, such as verbal exchanges, dance, and active listening, to express their ideas and build relationships with peers and adults.