par ALISSON DOMENICA OLIVO MENDEZ Il y a 3 années
363
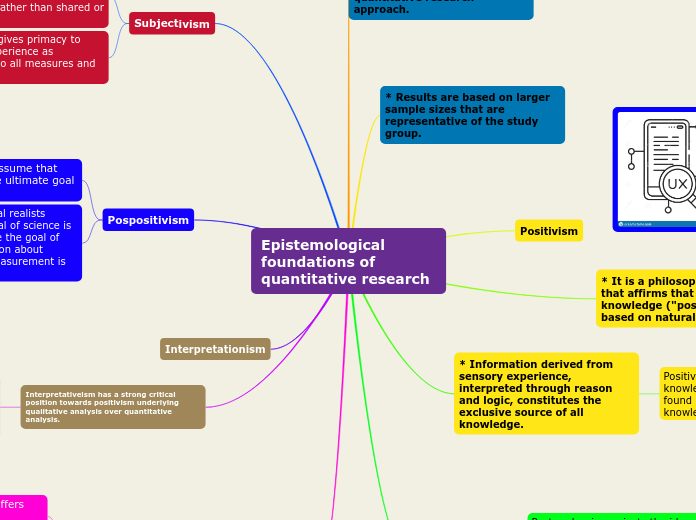
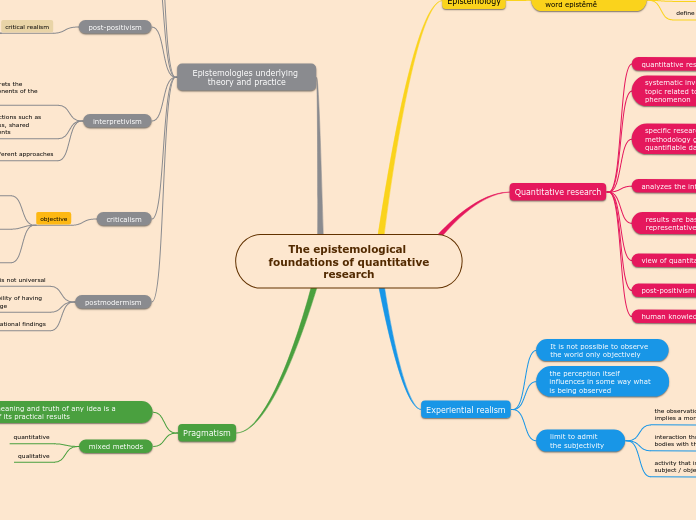
Epistemological foundations of quantitative research
The text explores different epistemological foundations in research methodologies, contrasting quantitative and qualitative approaches. It delves into positivism, a theory that bases knowledge on natural phenomena and emphasizes objective, measurable results from large sample sizes.