exponential and logarithmic functions
3.3 properties of logarithmic functions
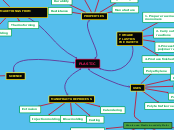
THERE ARE TWO MAIN PROPERTIES OF LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS
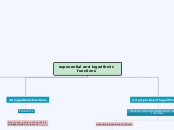
condensing logarithmic functions
the 3 properties of condensing:
power property
n logb mn = logb m^n
example:
3 log6 5=
log6 125
logb m - logb n = logb m/n
example:
ln (x^2+5)-x=
ln x+5/x
logb m + logb n = logb mn
example:
log 8 + log x + 4 log y=
log(8xy^4)
expanding logarithmic functions
the 3 properties of expanding:
power prperty
logb m^ n = n logb m
example:
log6 125=
3 log6 5
quotient property
logb m/n = logb m - logb n
example:
ln x+5/x=
ln (x^2+5)-x
product property
logb mn = logb m + logb n
example:
log(8xy^4)=
log 8 + log x + 4 log y
3.2 logarithmic functions
it follows a^x
for x>0, a>0, and a is not equal to 1
y=logax if and only if x=a^y
fro example: log base 3 of 9 is
equivalent to 3 to the power of 2
THERE ARE THREE TYPES OF LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS:
to the base e
also called natural
witten as ln x
to the base 10
also called common
written as log to the x
to any base except 10
written as logd to the x
3.1 exponential functions
the exponential function f with base a is denoted by f(x)=a^x
f(x)=a*b^2, where a is a non zero, b is positive,
and b is not equal to 1. the constant a is the initial
value and b is the base
THERE ARE TWO TYPES OF EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS:
exponential decay
a>0 and b<0
exponential growth
f(x)=a*b^x
a>0 and b>0