par Tanishq babbar Il y a 4 années
979
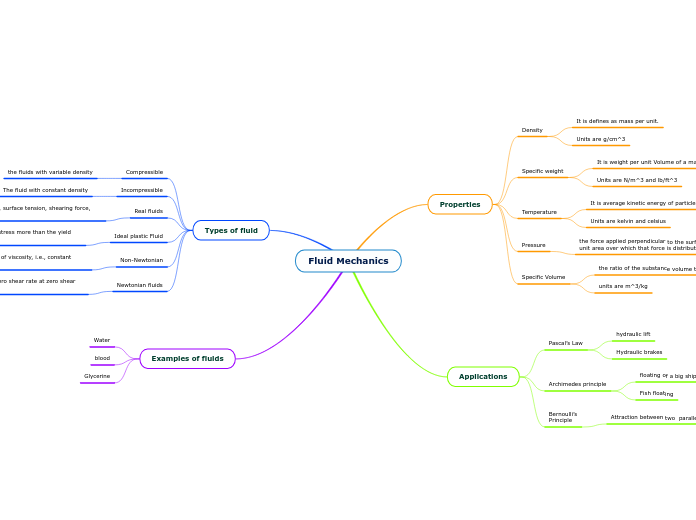
Fluid Mechanics
Fluid mechanics encompasses the study of fluids, including their properties and behaviors under various conditions. Fluids are substances like water, blood, and glycerine, each with unique characteristics.