par Anastasia Kungjaroen Il y a 5 années
602
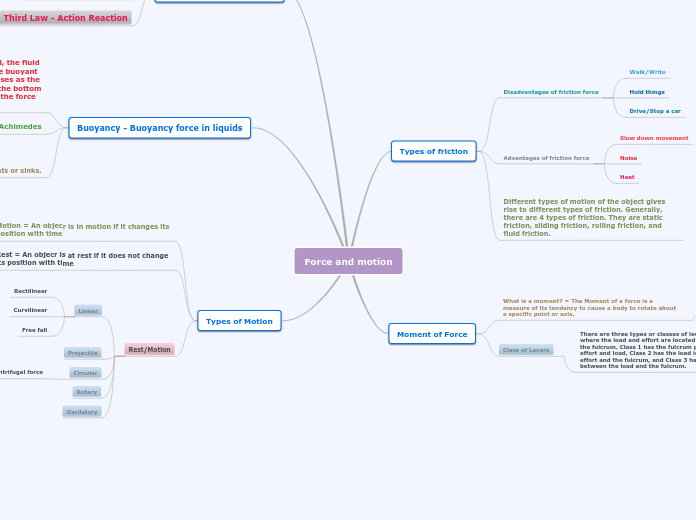
Force and motion
Several physical principles govern the behavior of objects in our world, such as friction, levers, and motion. Friction comes in various forms, including static, sliding, rolling, and fluid, each affecting how objects move.