Agnosias y apraxias
In linguistics, syntax is the set of rules, principles, and processes that govern the structure of sentences in a given language, usually including word order.
existen
A compound sentence is a sentence that has at least two independent clauses joined by a comma, semicolon or conjunction. An independent clause is a clause that has a subject and verb and forms a complete thought.
agnosias con menos frecuencias
Create your own compound sentences, using the coordinators above.
olfativas
gustativas
agnosias con más frecuencia
When independent clauses are joined with coordinators (also called coordinating conjunctions), commas and semicolons, they do more than just join the clauses. They add meaning and flow to your writing.
auditivas
visuales
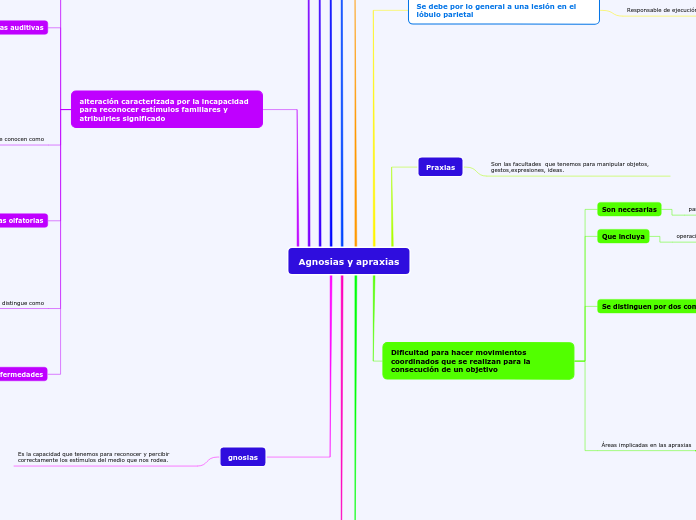
gnosias
Es la capacidad que tenemos para reconocer y percibir correctamente los estímulos del medio que nos rodea.
alteración caracterizada por la incapacidad para reconocer estímulos familiares y atribuirles significado
A complex sentence is a sentence that contains an independent clause and one or more dependent clauses.
An independent clause can stand alone as a sentence, but a dependent clause even though it has a subject and a verb cannot stand alone.
Agnosia para las enfermedades
An appositive clause follows another noun or noun phrase in apposition to it; that is, it provides information that further identifies or defines it.
Analgoagnosia
Somatoparafrenia
Misoplejia
Anosodiaforia
Asomatognosia
Anosognosia
se distingue como
la perdida del olfato
Agnosias olfatorias
The subject clause is a dependent clause that acts as a subject.
Agnosia anósmica
Anosmia sensorial
Cacosmia
Parosmia
Hiperosmia
Anosmia selectiva
Hiposmia
incapacidad para reconocer o diferenciar sonidos
Agnosias auditivas
A predicative clause may be introduced by conjunctions - that, whether, whether... or, as, as if, as though, because, lest, the way - or connectives.
The latter may be conjunctive pronouns - who, whoever, what, whatever, which - or conjunctive adverbs - where, wherever, when, whenever, how, why.
Agnosia espacial
Agnosia digital
Autotopagnosia
Barognosia
Agnosia táctil
Asterognosia
Agnosias somatosensoriales
Agnosia verba
Agnosia para los sonidos
Amusia
se conocen como
incapacidad para reconocer y comprender estímulos visuales
agnosias visuales
The object clause is a phrase on which a verb performs an action. It falls at the end of a sentence, and is governed by a verb or a preposition.
Agnosia para el movimiento
Alexia agnósica
Agnosia cromática
Prosopagnosia
Simultagnosia
agnosias para objetos
Puede haber agnosias unimodales o polimodales
según afecten a una o a varias modalidades
sensoriales
Consecuencia de accidentes vasculares
Están causadas por lesión de áreas
asociativas del córtex cerebral
Impiden la interpretación correcta del significado de los estímulos
Tipos de apraxias
Apraxia óptica
Apraxia bucofonatoria
Apraxia de la marcha
Apraxia del vestir
Apraxia constructiva
Apraxia ideatoria
Apraxia ideomotora
Dificultad para hacer movimientos coordinados que se realizan para la consecución de un objetivo
Áreas implicadas en las apraxias
Núcleos grises basales
Tálamo.
Cuerpo calloso.
Lóbulos temporales.
Lóbulos parietales.
Lóbulos occipitales
Área premotora suplementaria.
Área premotora
Se distinguen por dos componentes
Traditional grammar defines the object in a sentence as the entity that is acted upon by the subject.
sistema de produccion
The indirect object identifies the person/thing for whom/which the action of the verb is performed.
The indirect object is usually a person or a thing.
Su alteración
Provoca apraxia ideomotora.
Es responsable de llevar a cabo el programa motor
sistema conceptual
The direct object is the receiver of the action mentioned in the sentence.
Su alteración
provoca apraxia ideatoria.
Es el encargado de realizar el programa motor
Que incluya
The predicate of a sentence is the part that modifies the subject in some way. Because the subject is the person, place, or thing that a sentence is about, the predicate must contain a verb explaining what the subject does and can also include a modifier.
operaciones logicas
Son necesarias
The subject of a sentence is the person, place, thing, or idea that is doing or being something. You can find the subject of a sentence if you can find the verb.
Ask the question, 'Who or what 'verbs' or 'verbed'?' and the answer to that question is the subject.
para la información sensorial
Praxias
Son las facultades que tenemos para manipular objetos, gestos,expresiones, ideas.
Se debe por lo general a una lesión en el lóbulo parietal
Responsable de ejecución de movimientos motores complejos
Aparecen como resultado de lesiones o daños cerebrales